Artículo
Diffusion of sodium chloride in meat pork: Influence on its microstructure
Fecha de publicación:
12/2005
Editorial:
John Wiley & Sons Inc.
Revista:
Scanning
ISSN:
0161-0457
Idioma:
Inglés
Tipo de recurso:
Artículo publicado
Clasificación temática:
Resumen
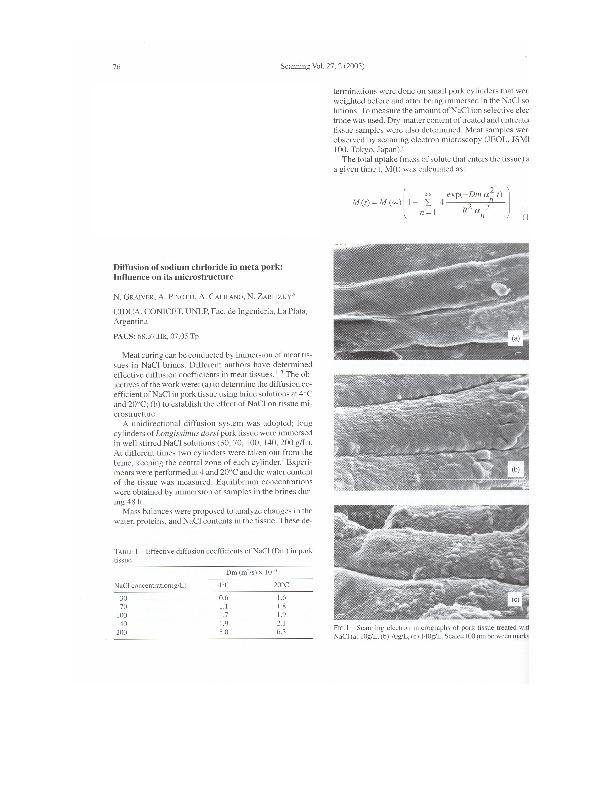
The objectives of the work were: a) to determine the diffusion coefficient of NaCl in pork tissue using brine solutions at 4°C and 20°C; b) to establish the effect of NaCl on tissue microstructure. A unidirectional diffusion system was adopted; long cylinders ofLongissimus dorsi pork tissue were immersed in well stirred NaCl solutions (30, 70, 100, 140, 200g/L). At different times two cylinders were taken out from the brine, keeping the central zone of each cylinder. Equilibrium concentrations were obtained by immersion ofsamples in the brines during 48 hours. Mass balances were proposedto analyze changes in the water, proteins, and NaCl contents in the tissue. Meat samples were observed by Scanning Electron Microscopy (JEOL, JSMP 100, Japan). The diffusion coefficients increased with NaCl concentration and temperature. NaCl uptake values expressed per mass of water in the tissue led to correct values of Dm. In contrast, when solute uptake values were expressed per mass of tissue without introducing the correction factors that consider the actual water content in the sample, erroneous overestimated Dm were obtained, higher than the diffusion coefficient of NaCl in water. The microestructural changes, as shown by the SEM micrographs, could explain the rise in the diffusion coefficients of NaCl at higher brine concentrations. At low concentrations of NaCl swelling of the fibers, and higher values of water content were observed. The phenomenon was reversed at higher NaCl concentrations; fiber volume decreased, the tissue lost its own water and proteins precipitated causing disruption in the matrix which facilitates salt penetration.
Palabras clave:
diffusion coefficients
,
curing salts
,
SEM
,
microstructure
Archivos asociados
Licencia
Identificadores
Colecciones
Articulos(CIDCA)
Articulos de CENTRO DE INV EN CRIOTECNOLOGIA DE ALIMENTOS (I)
Articulos de CENTRO DE INV EN CRIOTECNOLOGIA DE ALIMENTOS (I)
Citación
Graiver, Natalia Gisel; Pinotti, Adriana Noemi; Califano, Alicia Noemi; Zaritzky, Noemi Elisabet; Diffusion of sodium chloride in meat pork: Influence on its microstructure; John Wiley & Sons Inc.; Scanning; 27; 2; 12-2005; 76-77
Compartir