Mostrar el registro sencillo del ítem
dc.contributor.author
Graiver, Natalia Gisel

dc.contributor.author
Pinotti, Adriana Noemi

dc.contributor.author
Califano, Alicia Noemi

dc.contributor.author
Zaritzky, Noemi Elisabet

dc.date.available
2022-05-30T16:55:21Z
dc.date.issued
2005-12
dc.identifier.citation
Graiver, Natalia Gisel; Pinotti, Adriana Noemi; Califano, Alicia Noemi; Zaritzky, Noemi Elisabet; Diffusion of sodium chloride in meat pork: Influence on its microstructure; John Wiley & Sons Inc.; Scanning; 27; 2; 12-2005; 76-77
dc.identifier.issn
0161-0457
dc.identifier.uri
http://hdl.handle.net/11336/158496
dc.description.abstract
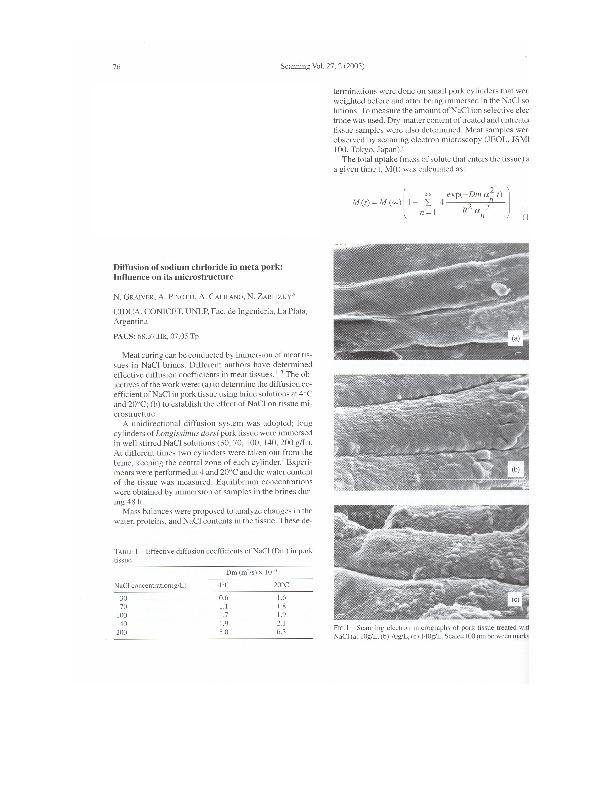
The objectives of the work were: a) to determine the diffusion coefficient of NaCl in pork tissue using brine solutions at 4°C and 20°C; b) to establish the effect of NaCl on tissue microstructure. A unidirectional diffusion system was adopted; long cylinders ofLongissimus dorsi pork tissue were immersed in well stirred NaCl solutions (30, 70, 100, 140, 200g/L). At different times two cylinders were taken out from the brine, keeping the central zone of each cylinder. Equilibrium concentrations were obtained by immersion ofsamples in the brines during 48 hours. Mass balances were proposedto analyze changes in the water, proteins, and NaCl contents in the tissue. Meat samples were observed by Scanning Electron Microscopy (JEOL, JSMP 100, Japan). The diffusion coefficients increased with NaCl concentration and temperature. NaCl uptake values expressed per mass of water in the tissue led to correct values of Dm. In contrast, when solute uptake values were expressed per mass of tissue without introducing the correction factors that consider the actual water content in the sample, erroneous overestimated Dm were obtained, higher than the diffusion coefficient of NaCl in water. The microestructural changes, as shown by the SEM micrographs, could explain the rise in the diffusion coefficients of NaCl at higher brine concentrations. At low concentrations of NaCl swelling of the fibers, and higher values of water content were observed. The phenomenon was reversed at higher NaCl concentrations; fiber volume decreased, the tissue lost its own water and proteins precipitated causing disruption in the matrix which facilitates salt penetration.
dc.format
application/pdf
dc.language.iso
eng
dc.publisher
John Wiley & Sons Inc.

dc.rights
info:eu-repo/semantics/openAccess
dc.rights.uri
https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/2.5/ar/
dc.subject
diffusion coefficients
dc.subject
curing salts
dc.subject
SEM
dc.subject
microstructure
dc.subject.classification
Alimentos y Bebidas

dc.subject.classification
Otras Ingenierías y Tecnologías

dc.subject.classification
INGENIERÍAS Y TECNOLOGÍAS

dc.title
Diffusion of sodium chloride in meat pork: Influence on its microstructure
dc.type
info:eu-repo/semantics/article
dc.type
info:ar-repo/semantics/artículo
dc.type
info:eu-repo/semantics/publishedVersion
dc.date.updated
2022-05-12T07:56:43Z
dc.journal.volume
27
dc.journal.number
2
dc.journal.pagination
76-77
dc.journal.pais
Estados Unidos

dc.journal.ciudad
Mahwah
dc.description.fil
Fil: Graiver, Natalia Gisel. Provincia de Buenos Aires. Gobernación. Comisión de Investigaciones Científicas. Centro de Investigación y Desarrollo en Criotecnología de Alimentos. Consejo Nacional de Investigaciones Científicas y Técnicas. Centro Científico Tecnológico Conicet - La Plata. Centro de Investigación y Desarrollo en Criotecnología de Alimentos. Universidad Nacional de La Plata. Facultad de Ciencias Exactas. Centro de Investigación y Desarrollo en Criotecnología de Alimentos; Argentina
dc.description.fil
Fil: Pinotti, Adriana Noemi. Provincia de Buenos Aires. Gobernación. Comisión de Investigaciones Científicas. Centro de Investigación y Desarrollo en Criotecnología de Alimentos. Consejo Nacional de Investigaciones Científicas y Técnicas. Centro Científico Tecnológico Conicet - La Plata. Centro de Investigación y Desarrollo en Criotecnología de Alimentos. Universidad Nacional de La Plata. Facultad de Ciencias Exactas. Centro de Investigación y Desarrollo en Criotecnología de Alimentos; Argentina
dc.description.fil
Fil: Califano, Alicia Noemi. Provincia de Buenos Aires. Gobernación. Comisión de Investigaciones Científicas. Centro de Investigación y Desarrollo en Criotecnología de Alimentos. Consejo Nacional de Investigaciones Científicas y Técnicas. Centro Científico Tecnológico Conicet - La Plata. Centro de Investigación y Desarrollo en Criotecnología de Alimentos. Universidad Nacional de La Plata. Facultad de Ciencias Exactas. Centro de Investigación y Desarrollo en Criotecnología de Alimentos; Argentina
dc.description.fil
Fil: Zaritzky, Noemi Elisabet. Provincia de Buenos Aires. Gobernación. Comisión de Investigaciones Científicas. Centro de Investigación y Desarrollo en Criotecnología de Alimentos. Consejo Nacional de Investigaciones Científicas y Técnicas. Centro Científico Tecnológico Conicet - La Plata. Centro de Investigación y Desarrollo en Criotecnología de Alimentos. Universidad Nacional de La Plata. Facultad de Ciencias Exactas. Centro de Investigación y Desarrollo en Criotecnología de Alimentos; Argentina. Universidad Nacional de La Plata. Facultad de Ingeniería. Departamento de Ingeniería Química; Argentina
dc.journal.title
Scanning

Archivos asociados