Artículo
PI3K/Akt cooperates with oncogenic Notch by inducing nitric oxide-dependent inflammation
Villegas, Santiago Nahuel ; Gombos, Rita; García López, Lucia; Gutiérrez Pérez, Irene; García Castillo, Jesús; Vallejo, Diana Marcela; Da Ros, Vanina Gabriela
; Gombos, Rita; García López, Lucia; Gutiérrez Pérez, Irene; García Castillo, Jesús; Vallejo, Diana Marcela; Da Ros, Vanina Gabriela ; Ballesta Illán, Esther; Mihály, József; Dominguez, Maria
; Ballesta Illán, Esther; Mihály, József; Dominguez, Maria
 ; Gombos, Rita; García López, Lucia; Gutiérrez Pérez, Irene; García Castillo, Jesús; Vallejo, Diana Marcela; Da Ros, Vanina Gabriela
; Gombos, Rita; García López, Lucia; Gutiérrez Pérez, Irene; García Castillo, Jesús; Vallejo, Diana Marcela; Da Ros, Vanina Gabriela ; Ballesta Illán, Esther; Mihály, József; Dominguez, Maria
; Ballesta Illán, Esther; Mihály, József; Dominguez, Maria
Fecha de publicación:
03/2018
Editorial:
Elsevier B.V.
Revista:
Cell Reports
ISSN:
2211-1247
Idioma:
Inglés
Tipo de recurso:
Artículo publicado
Clasificación temática:
Resumen
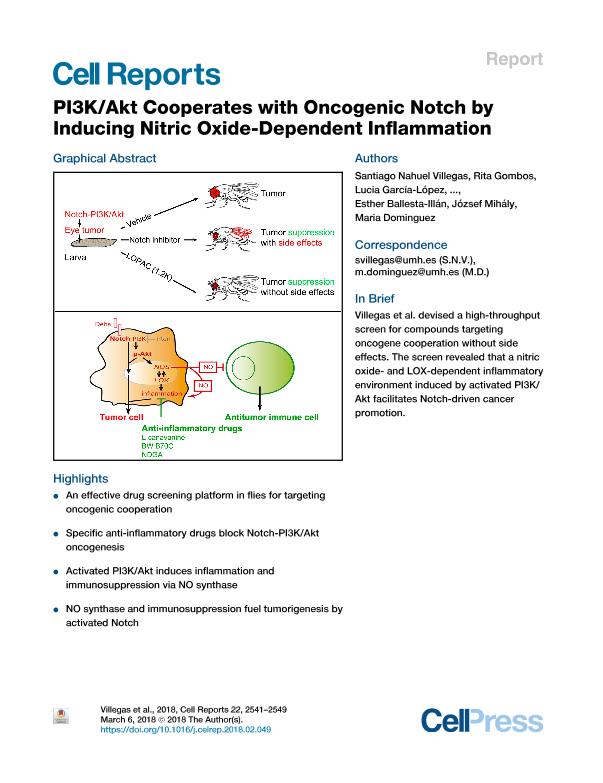
The PI3K/Akt signaling pathway, Notch, and other oncogenes cooperate in the induction of aggressive cancers. Elucidating how the PI3K/Akt pathway facilitates tumorigenesis by other oncogenes may offer opportunities to develop drugs with fewer side effects than those currently available. Here, using an unbiased in vivo chemical genetic screen in Drosophila, we identified compounds that inhibit the activity of proinflammatory enzymes nitric oxide synthase (NOS) and lipoxygenase (LOX) as selective suppressors of Notch-PI3K/Akt cooperative oncogenesis. Tumor silencing of NOS and LOX signaling mirrored the antitumor effect of the hit compounds, demonstrating their participation in Notch-PI3K/Akt-induced tumorigenesis. Oncogenic PI3K/Akt signaling triggered inflammation and immunosuppression via aberrant NOS expression. Accordingly, activated Notch tumorigenesis was fueled by hampering the immune response or by NOS overexpression to mimic a protumorigenic environment. Our lead compound, the LOX inhibitor BW B70C, also selectively killed human leukemic cells by dampening the NOTCH1-PI3K/AKT-eNOS axis.
Palabras clave:
BW B70C
,
CANCER
,
CHEMICAL SCREEN
,
DROSOPHILA
,
INFLAMMATION
,
LOX
,
NOS
,
NOTCH
,
PTEN/PI3K/AKT
,
T-ALL
Archivos asociados
Licencia
Identificadores
Colecciones
Articulos(IBYME)
Articulos de INST.DE BIOLOGIA Y MEDICINA EXPERIMENTAL (I)
Articulos de INST.DE BIOLOGIA Y MEDICINA EXPERIMENTAL (I)
Citación
Villegas, Santiago Nahuel; Gombos, Rita; García López, Lucia; Gutiérrez Pérez, Irene; García Castillo, Jesús; et al.; PI3K/Akt cooperates with oncogenic Notch by inducing nitric oxide-dependent inflammation; Elsevier B.V.; Cell Reports; 22; 10; 3-2018; 2541-2549
Compartir
Altmétricas