Artículo
Modulation of Tau Isoforms Imbalance Precludes Tau Pathology and Cognitive Decline in a Mouse Model of Tauopathy
Espindola, Sonia Lorena ; Damianich, Ana
; Damianich, Ana ; Alvarez, Rodrigo Javier
; Alvarez, Rodrigo Javier ; Sartor, Manuela
; Sartor, Manuela ; Belforte, Juan Emilio
; Belforte, Juan Emilio ; Ferrario, Juan Esteban
; Ferrario, Juan Esteban ; Gallo, Jean Marc; Avale, Maria Elena
; Gallo, Jean Marc; Avale, Maria Elena
 ; Damianich, Ana
; Damianich, Ana ; Alvarez, Rodrigo Javier
; Alvarez, Rodrigo Javier ; Sartor, Manuela
; Sartor, Manuela ; Belforte, Juan Emilio
; Belforte, Juan Emilio ; Ferrario, Juan Esteban
; Ferrario, Juan Esteban ; Gallo, Jean Marc; Avale, Maria Elena
; Gallo, Jean Marc; Avale, Maria Elena
Fecha de publicación:
04/2018
Editorial:
Elsevier
Revista:
Cell Reports
ISSN:
2211-1247
Idioma:
Inglés
Tipo de recurso:
Artículo publicado
Clasificación temática:
Resumen
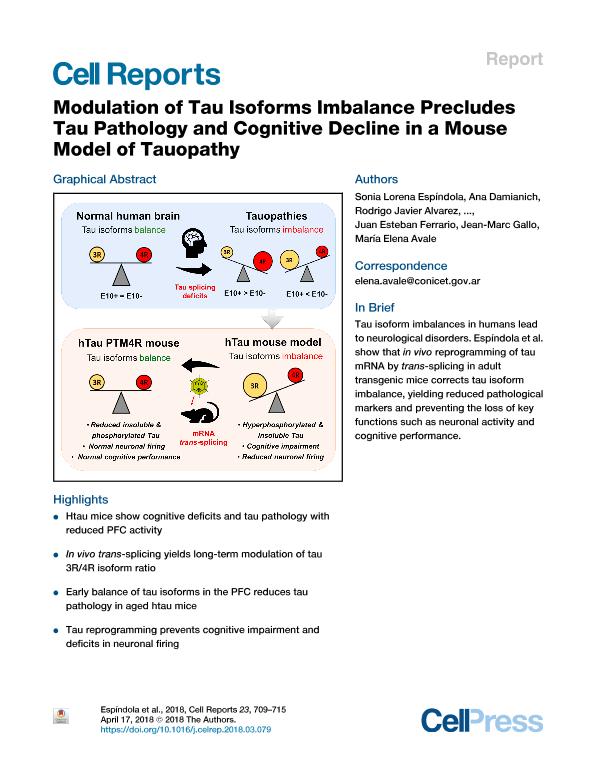
The microtubule-associated protein tau regulates myriad neuronal functions, such as microtubule dynamics, axonal transport and neurite outgrowth. Tauopathies are neurodegenerative disorders characterized by the abnormal metabolism of tau, which accumulates as insoluble neuronal deposits. The adult human brain contains equal amounts of tau isoforms with three (3R) or four (4R) repeats of microtubule-binding domains, derived from the alternative splicing of exon 10 (E10) in the tau transcript. Several tauopathies are associated with imbalances of tau isoforms, due to splicing deficits. Here, we used a trans-splicing strategy to shift the inclusion of E10 in a mouse model of tauopathy that produces abnormal excess of 3R tau. Modulating the 3R/4R ratio in the prefrontal cortex led to a significant reduction of pathological tau accumulation concomitant with improvement of neuronal firing and reduction of cognitive impairments. Our results suggest promising potential for the use of RNA reprogramming in human neurodegenerative diseases. Tau isoform imbalances in humans lead to neurological disorders. Espíndola et al. show that in vivo reprogramming of tau mRNA by trans-splicing in adult transgenic mice corrects tau isoform imbalance, yielding reduced pathological markers and preventing the loss of key functions such as neuronal activity and cognitive performance.
Palabras clave:
ALTERNATIVE SPLICING
,
DEMENTIA
,
GENE THERAPY
,
MAPT
,
NEURODEGENERATION
,
TAUOPATHY
Archivos asociados
Licencia
Identificadores
Colecciones
Articulos(IFIBIO HOUSSAY)
Articulos de INSTITUTO DE FISIOLOGIA Y BIOFISICA BERNARDO HOUSSAY
Articulos de INSTITUTO DE FISIOLOGIA Y BIOFISICA BERNARDO HOUSSAY
Articulos(INGEBI)
Articulos de INST.DE INVEST.EN ING.GENETICA Y BIOL.MOLECULAR "DR. HECTOR N TORRES"
Articulos de INST.DE INVEST.EN ING.GENETICA Y BIOL.MOLECULAR "DR. HECTOR N TORRES"
Articulos(ININFA)
Articulos de INST.DE INVEST.FARMACOLOGICAS (I)
Articulos de INST.DE INVEST.FARMACOLOGICAS (I)
Citación
Espindola, Sonia Lorena; Damianich, Ana; Alvarez, Rodrigo Javier; Sartor, Manuela; Belforte, Juan Emilio; et al.; Modulation of Tau Isoforms Imbalance Precludes Tau Pathology and Cognitive Decline in a Mouse Model of Tauopathy; Elsevier; Cell Reports; 23; 3; 4-2018; 709-715
Compartir
Altmétricas