Artículo
The Emergence of the Spatial Structure of Tectal Spontaneous Activity Is Independent of Visual Inputs
Pietri, Thomas; Romano, Sebastián A.; Pérez Schuster, Verónica ; Boulanger Weill, Jonathan; Candat, Virginie; Sumbre, Germán
; Boulanger Weill, Jonathan; Candat, Virginie; Sumbre, Germán
 ; Boulanger Weill, Jonathan; Candat, Virginie; Sumbre, Germán
; Boulanger Weill, Jonathan; Candat, Virginie; Sumbre, Germán
Fecha de publicación:
05/2017
Editorial:
Elsevier
Revista:
Cell Reports
ISSN:
2211-1247
Idioma:
Inglés
Tipo de recurso:
Artículo publicado
Clasificación temática:
Resumen
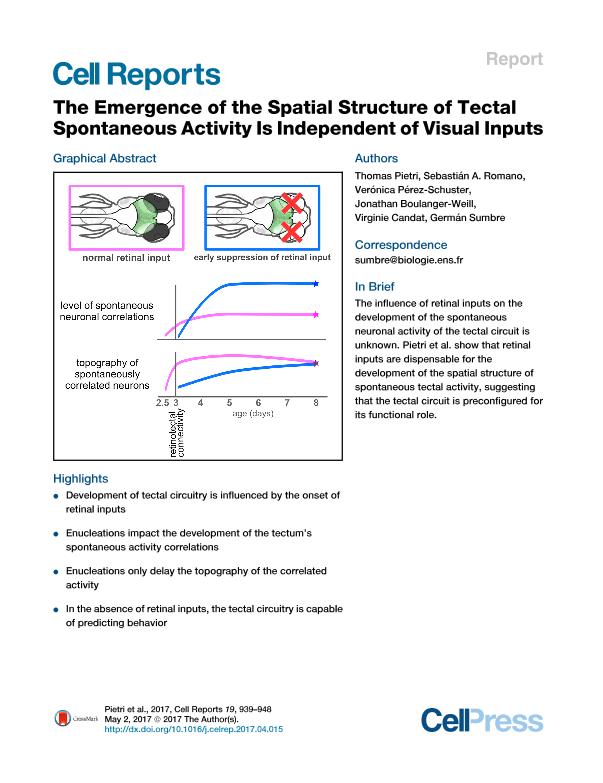
The brain is spontaneously active, even in the absence of sensory stimulation. The functionally mature zebrafish optic tectum shows spontaneous activity patterns reflecting a functional connectivity adapted for the circuit's functional role and predictive of behavior. However, neither the emergence of these patterns during development nor the role of retinal inputs in their maturation has been characterized. Using two-photon calcium imaging, we analyzed spontaneous activity in intact and enucleated zebrafish larvae throughout tectum development. At the onset of retinotectal connections, intact larvae showed major changes in the spatiotemporal structure of spontaneous activity. Although the absence of retinal inputs had a significant impact on the development of the temporal structure, the tectum was still capable of developing a spatial structure associated with the circuit's functional roles and predictive of behavior. We conclude that neither visual experience nor intrinsic retinal activity is essential for the emergence of a spatially structured functional circuit.
Archivos asociados
Licencia
Identificadores
Colecciones
Articulos(IBIOBA - MPSP)
Articulos de INST. D/INV.EN BIOMED.DE BS AS-CONICET-INST. PARTNER SOCIEDAD MAX PLANCK
Articulos de INST. D/INV.EN BIOMED.DE BS AS-CONICET-INST. PARTNER SOCIEDAD MAX PLANCK
Articulos(IFIBYNE)
Articulos de INST.DE FISIOL., BIOL.MOLECULAR Y NEUROCIENCIAS
Articulos de INST.DE FISIOL., BIOL.MOLECULAR Y NEUROCIENCIAS
Citación
Pietri, Thomas; Romano, Sebastián A.; Pérez Schuster, Verónica; Boulanger Weill, Jonathan; Candat, Virginie; et al.; The Emergence of the Spatial Structure of Tectal Spontaneous Activity Is Independent of Visual Inputs; Elsevier; Cell Reports; 19; 5; 5-2017; 939-948
Compartir
Altmétricas