Artículo
Protein Kinase C Epsilon Cooperates with PTEN Loss for Prostate Tumorigenesis through the CXCL13-CXCR5 Pathway
Garg, Rachana; Blando, Jorge M.; Perez, Carlos J.; Abba, Martín Carlos ; Benavides Agredo, Fernando Andres; Kazanietz, Marcelo Gabriel
; Benavides Agredo, Fernando Andres; Kazanietz, Marcelo Gabriel
 ; Benavides Agredo, Fernando Andres; Kazanietz, Marcelo Gabriel
; Benavides Agredo, Fernando Andres; Kazanietz, Marcelo Gabriel
Fecha de publicación:
04/2017
Editorial:
Elsevier Science
Revista:
Cell Reports
ISSN:
2211-1247
Idioma:
Inglés
Tipo de recurso:
Artículo publicado
Clasificación temática:
Resumen
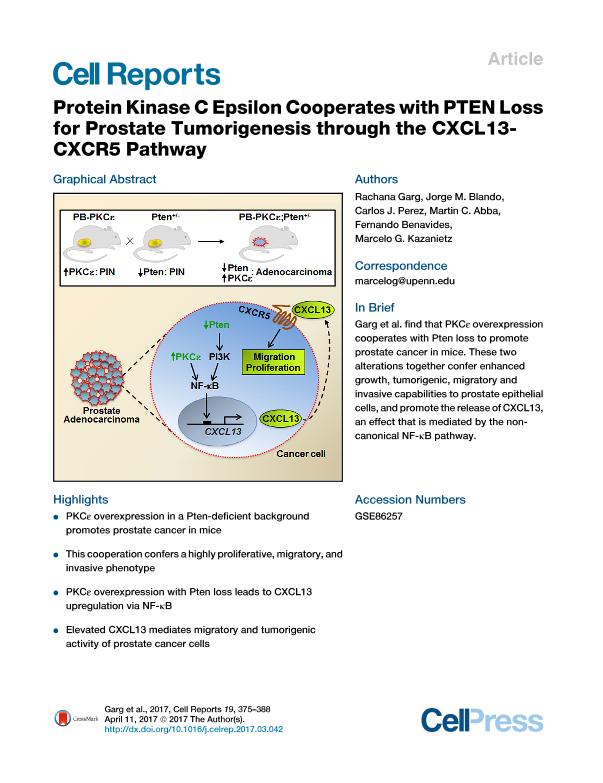
PKCε, an oncogenic member of the PKC family, is aberrantly overexpressed in epithelial cancers. To date, little is known about functional interactions of PKCε with other genetic alterations, as well as the effectors contributing to its tumorigenic and metastatic phenotype. Here, we demonstrate that PKCε cooperates with the loss of the tumor suppressor Pten for the development of prostate cancer in a mouse model. Mechanistic analysis revealed that PKCε overexpression and Pten loss individually and synergistically upregulate the production of the chemokine CXCL13, which involves the transcriptional activation of the CXCL13 gene via the non-canonical nuclear factor κB (NF-κB) pathway. Notably, targeted disruption of CXCL13 or its receptor, CXCR5, in prostate cancer cells impaired their migratory and tumorigenic properties. In addition to providing evidence for an autonomous vicious cycle driven by PKCε, our studies identified a compelling rationale for targeting the CXCL13-CXCR5 axis for prostate cancer treatment.
Palabras clave:
Cxcl13
,
Cxcr5
,
Migration
,
Nf-ΚB
,
PkcΕ
,
Proliferation
,
Prostate Cancer
,
Pten
,
Transgenic Mice
Archivos asociados
Licencia
Identificadores
Colecciones
Articulos(CCT - LA PLATA)
Articulos de CTRO.CIENTIFICO TECNOL.CONICET - LA PLATA
Articulos de CTRO.CIENTIFICO TECNOL.CONICET - LA PLATA
Citación
Garg, Rachana; Blando, Jorge M.; Perez, Carlos J.; Abba, Martín Carlos; Benavides Agredo, Fernando Andres; et al.; Protein Kinase C Epsilon Cooperates with PTEN Loss for Prostate Tumorigenesis through the CXCL13-CXCR5 Pathway; Elsevier Science; Cell Reports; 19; 2; 4-2017; 375-388
Compartir
Altmétricas