Artículo
Ibrutinib impairs the phagocytosis of rituximab-coated leukemic cells from chronic lymphocytic leukemia patients by human macrophages
Borge, Mercedes ; Almejún, María Belén
; Almejún, María Belén ; Podaza, Enrique Arturo
; Podaza, Enrique Arturo ; Colado, Ana
; Colado, Ana ; Fernández Grecco, Horacio; Cabrejo, María; Bezares, Raimundo F.; Giordano, Mirta Nilda
; Fernández Grecco, Horacio; Cabrejo, María; Bezares, Raimundo F.; Giordano, Mirta Nilda ; Gamberale, Romina
; Gamberale, Romina
 ; Almejún, María Belén
; Almejún, María Belén ; Podaza, Enrique Arturo
; Podaza, Enrique Arturo ; Colado, Ana
; Colado, Ana ; Fernández Grecco, Horacio; Cabrejo, María; Bezares, Raimundo F.; Giordano, Mirta Nilda
; Fernández Grecco, Horacio; Cabrejo, María; Bezares, Raimundo F.; Giordano, Mirta Nilda ; Gamberale, Romina
; Gamberale, Romina
Fecha de publicación:
01/2015
Editorial:
Ferrata Storti Foundation
Revista:
Haematologica
ISSN:
0390-6078
e-ISSN:
1592-8721
Idioma:
Inglés
Tipo de recurso:
Artículo publicado
Clasificación temática:
Resumen
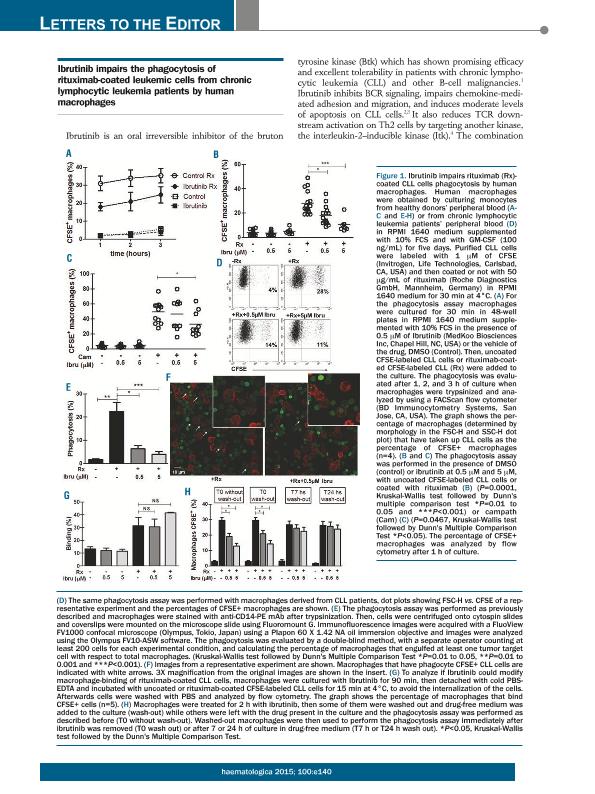
We have read with great interest the recent article of Kohrt, H.E. et al1 showing that Ibrutinib prevented NK cell mediated cytotoxicity of antibody-coated CLL cells in vitro. They also found that the concurrent treatment with Ibrutinib and rituximab or trastuzumab reduces the therapeutic efficacy of both anti-CD20 antibodies in a mouse model, while the sequential treatment with Ibrutinib and rituximab restored its anti-lymphoma activity. Since macrophages are the most important effector cells in CD20-directed cytotoxicity in murine models2,3 and they probably play a key role in human anti-CD20 therapy4,5, we determined whether Ibrutinib interferes the capacity of human macrophages to mediate phagocytosis of rituximab-coated CLL cells. To address this issue, macrophages differentiated from healthy peripheral blood monocytes were treated with or without Ibrutinib for 30 minutes and then cultured for 1, 2 or 3 hours with CFSE-labeled CLL cells or rituximab-coated CFSE-labeled CLL cells. Then, cells were tripsinized and the proportion of macrophages that have taken up CFSE-labeled CLL cells (CFSE+ macrophages) were scored by flow cytometry and verified using confocal microscopy, as previously described6. As expected, we found that the cultures with rituximab-coated CLL cells showed the highest percentage of CFSE+ macrophages, which increase in a time dependent manner (open circles in Figure 1A). Ibrutinib was able to reduce these values in all the times evaluated (solid circles in Figure 1A). Low percentages of CFSE+ macrophages were obtained in cultures with uncoated CLL cells, which were not modified by Ibrutinib (open and solid squares in Figure 1A). In addition, we found that Ibrutinib diminishes the percentage of CFSE+ macrophages in the cultures with rituximab-coated cells in a dose dependent manner (Figure 1B), which was not associated to a decreased viability of the macrophages (not shown). Moreover, the inhibitory effect of Ibrutinib was not limited to rituximab since comparable results were obtained when campath-coated CFSE-labeled CLL cells were employed (Figure 1C). Similar results were found when macrophages from CLL patients were used: mean±SE of the % of CFSE+ macrophages: 26.8 ± 2.1 vs, 17.3 ± 2.7 vs 10.8 ± 0.7 for rituximab-coated CFSE-labeled CLL cells alone, with 0.5μM or 5μM of Ibrutinib (n= 6). Representative dot plots are shown in Figure 1D. The results obtained by flow cytometry analysis were validated by confocal microscopy quantifying the number of macrophages that engulfed at least one tumor target cell (Figure 1E). A representative experiment is shown in Figure 1F. In addition, by performing a binding assay at 4oC, we confirmed that Ibrutinib did not reduce the binding of rituximab-coated CFSE-labeled CLL cells to macrophages (Figure 1G). Interestingly, while the presence of Ibrutinib during the assay impairs the phagocytosis of rituximab-coated CLL cells, when Ibrutinib was washed out, macrophages recovered their phagocytic capacity in a time-dependent manner (Figure 1H). In conclusion we found that the presence of Ibrutinib impairs the phagocytosis of rituximab-opsonized CLL cells by human macrophages, which was restored when the inhibitor was removed from the cultures. Our results, and those obtained by Kohrt et al1 suggest that the sequential administration of Ibrutinib followed by rituximab, and not the concurrent treatment of the patients with these agents, might enhance their anti-tumor activity in vivo.
Palabras clave:
Ibrutinib
,
Phagocytosis
,
Rituximab-Dependent
Archivos asociados
Licencia
Identificadores
Colecciones
Articulos(IMEX)
Articulos de INST.DE MEDICINA EXPERIMENTAL
Articulos de INST.DE MEDICINA EXPERIMENTAL
Citación
Borge, Mercedes; Almejún, María Belén; Podaza, Enrique Arturo; Colado, Ana; Fernández Grecco, Horacio; et al.; Ibrutinib impairs the phagocytosis of rituximab-coated leukemic cells from chronic lymphocytic leukemia patients by human macrophages; Ferrata Storti Foundation; Haematologica; 100; 4; 1-2015; 1-3
Compartir
Altmétricas