Mostrar el registro sencillo del ítem
dc.contributor.author
Zang, Xiaoling
dc.contributor.author
Jones, Christina M.
dc.contributor.author
Long, Tran Q.
dc.contributor.author
Monge, Maria Eugenia

dc.contributor.author
Zhou, Manshui
dc.contributor.author
DeEtte Walker, L.
dc.contributor.author
Mezencev, Roman
dc.contributor.author
Gray, Alexander
dc.contributor.author
McDonald, John F.
dc.contributor.author
Fernandez, Facundo M.
dc.date.available
2017-12-15T20:16:53Z
dc.date.issued
2014-06
dc.identifier.citation
Fernandez, Facundo M.; McDonald, John F.; Gray, Alexander; Mezencev, Roman; DeEtte Walker, L.; Zhou, Manshui; et al.; Feasibility of Detecting Prostate Cancer by Ultraperformance Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry Serum Metabolomics; American Chemical Society; Journal of Proteome Research; 13; 7; 6-2014; 3444-3454
dc.identifier.issn
1535-3893
dc.identifier.uri
http://hdl.handle.net/11336/30813
dc.description.abstract
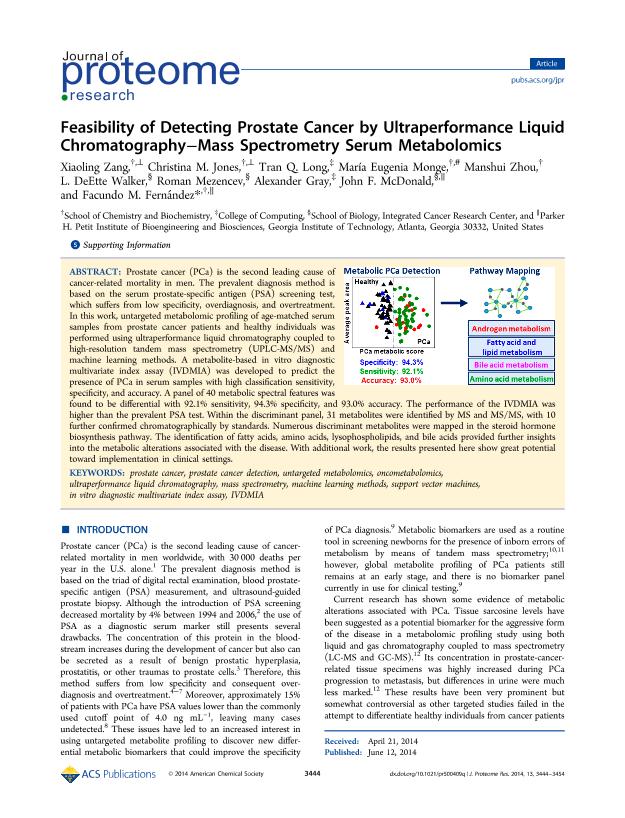
Prostate cancer (PCa) is the second leading cause of cancer-related mortality in men. The prevalent diagnosis method is based on the serum prostate-specific antigen (PSA) screening test, which suffers from low specificity, overdiagnosis, and overtreatment. In this work, untargeted metabolomic profiling of age-matched serum samples from prostate cancer patients and healthy individuals was performed using ultraperformance liquid chromatography coupled to high-resolution tandem mass spectrometry (UPLC-MS/MS) and machine learning methods. A metabolite-based in vitro diagnostic multivariate index assay (IVDMIA) was developed to predict the presence of PCa in serum samples with high classification sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy. A panel of 40 metabolic spectral features was found to be differential with 92.1% sensitivity, 94.3% specificity, and 93.0% accuracy. The performance of the IVDMIA was higher than the prevalent PSA test. Within the discriminant panel, 31 metabolites were identified by MS and MS/MS, with 10 further confirmed chromatographically by standards. Numerous discriminant metabolites were mapped in the steroid hormone biosynthesis pathway. The identification of fatty acids, amino acids, lysophospholipids, and bile acids provided further insights into the metabolic alterations associated with the disease. With additional work, the results presented here show great potential toward implementation in clinical settings.
dc.format
application/pdf
dc.language.iso
eng
dc.publisher
American Chemical Society

dc.rights
info:eu-repo/semantics/openAccess
dc.rights.uri
https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/2.5/ar/
dc.subject
Prostate Cancer
dc.subject
Prostate Cancer Detection
dc.subject
Untargeted Metabolomics
dc.subject
Oncometabolomics
dc.subject
Ultraperformance Liquid Chromatography
dc.subject
Mass Spectrometry
dc.subject
Machine Learning Methods
dc.subject
Support Vector Machines
dc.subject
In Vitro Diagnostic Multivariate Index Assay
dc.subject
Ivdmia
dc.subject.classification
Otras Ciencias Químicas

dc.subject.classification
Ciencias Químicas

dc.subject.classification
CIENCIAS NATURALES Y EXACTAS

dc.title
Feasibility of Detecting Prostate Cancer by Ultraperformance Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry Serum Metabolomics
dc.type
info:eu-repo/semantics/article
dc.type
info:ar-repo/semantics/artículo
dc.type
info:eu-repo/semantics/publishedVersion
dc.date.updated
2017-12-11T15:04:13Z
dc.journal.volume
13
dc.journal.number
7
dc.journal.pagination
3444-3454
dc.journal.pais
Estados Unidos

dc.description.fil
Fil: Zang, Xiaoling. Georgia Institute of Techology; Estados Unidos
dc.description.fil
Fil: Jones, Christina M.. Georgia Institute of Techology; Estados Unidos
dc.description.fil
Fil: Long, Tran Q.. Georgia Institute of Techology; Estados Unidos
dc.description.fil
Fil: Monge, Maria Eugenia. Georgia Institute of Techology; Estados Unidos. Consejo Nacional de Investigaciones Científicas y Técnicas; Argentina
dc.description.fil
Fil: Zhou, Manshui. Georgia Institute of Techology; Estados Unidos
dc.description.fil
Fil: DeEtte Walker, L.. Georgia Institute of Techology; Estados Unidos
dc.description.fil
Fil: Mezencev, Roman. Georgia Institute of Techology; Estados Unidos
dc.description.fil
Fil: Gray, Alexander. Georgia Institute of Techology; Estados Unidos
dc.description.fil
Fil: McDonald, John F.. Georgia Institute of Techology; Estados Unidos
dc.description.fil
Fil: Fernandez, Facundo M.. Georgia Institute of Techology; Estados Unidos
dc.journal.title
Journal of Proteome Research

dc.relation.alternativeid
info:eu-repo/semantics/altIdentifier/doi/http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/pr500409q
dc.relation.alternativeid
info:eu-repo/semantics/altIdentifier/url/http://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/pr500409q
Archivos asociados