Mostrar el registro sencillo del ítem
dc.contributor.author
Nuno Perez, Alvaro
dc.contributor.author
Trusel, Massimo
dc.contributor.author
Lalive, Arnaud L.
dc.contributor.author
Congiu, Mauro
dc.contributor.author
Gastaldo, Denise
dc.contributor.author
Tchenio, Anna
dc.contributor.author
Lecca, Salvatore
dc.contributor.author
Soiza Reilly, Mariano

dc.contributor.author
Bagni, Claudia
dc.contributor.author
Mameli, Manuel
dc.date.available
2022-10-28T10:33:01Z
dc.date.issued
2021-03
dc.identifier.citation
Nuno Perez, Alvaro; Trusel, Massimo; Lalive, Arnaud L.; Congiu, Mauro; Gastaldo, Denise; et al.; Stress undermines reward-guided cognitive performance through synaptic depression in the lateral habenula; Cell Press; Neuron; 109; 6; 3-2021; 947-956
dc.identifier.issn
0896-6273
dc.identifier.uri
http://hdl.handle.net/11336/175287
dc.description.abstract
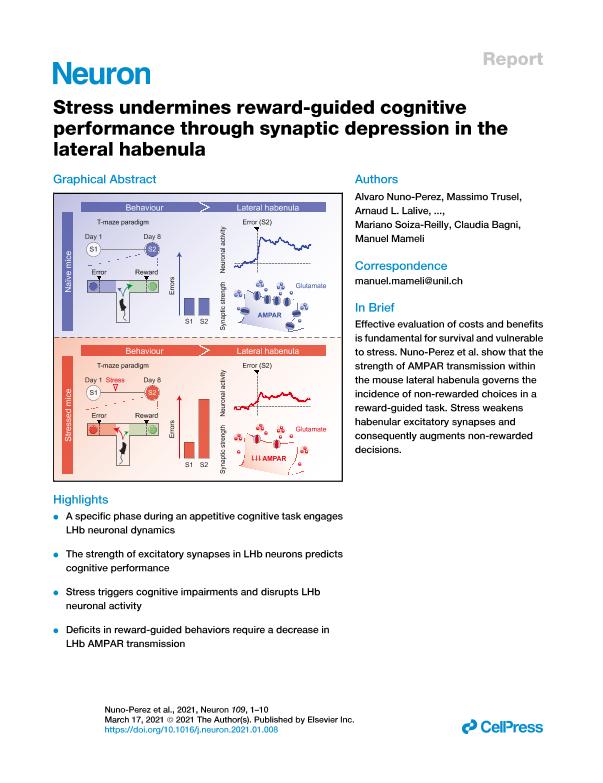
Weighing alternatives during reward pursuit is a vital cognitive computation that, when disrupted by stress, yields aspects of neuropsychiatric disorders. To examine the neural mechanisms underlying these phenomena, we employed a behavioral task in which mice were confronted by a reward and its omission (i.e., error). The experience of error outcomes engaged neuronal dynamics within the lateral habenula (LHb), a subcortical structure that supports appetitive behaviors and is susceptible to stress. A high incidence of errors predicted low strength of habenular excitatory synapses. Accordingly, stressful experiences increased error choices while decreasing glutamatergic neurotransmission onto LHb neurons. This synaptic adaptation required a reduction in postsynaptic AMPA receptors (AMPARs), irrespective of the anatomical source of glutamate. Bidirectional control of habenular AMPAR transmission recapitulated and averted stress-driven cognitive deficits. Thus, a subcortical synaptic mechanism vulnerable to stress underlies behavioral efficiency during cognitive performance.
dc.format
application/pdf
dc.language.iso
eng
dc.publisher
Cell Press

dc.rights
info:eu-repo/semantics/openAccess
dc.rights.uri
https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/2.5/ar/
dc.subject
AMPA RECEPTORS
dc.subject
LATERAL HABENULA
dc.subject
REWARD-GUIDED BEHAVIORS
dc.subject
STRESS
dc.subject.classification
Neurociencias

dc.subject.classification
Medicina Básica

dc.subject.classification
CIENCIAS MÉDICAS Y DE LA SALUD

dc.title
Stress undermines reward-guided cognitive performance through synaptic depression in the lateral habenula
dc.type
info:eu-repo/semantics/article
dc.type
info:ar-repo/semantics/artículo
dc.type
info:eu-repo/semantics/publishedVersion
dc.date.updated
2022-09-23T14:26:42Z
dc.journal.volume
109
dc.journal.number
6
dc.journal.pagination
947-956
dc.journal.pais
Estados Unidos

dc.description.fil
Fil: Nuno Perez, Alvaro. Universite de Lausanne; Suiza
dc.description.fil
Fil: Trusel, Massimo. Universite de Lausanne; Suiza
dc.description.fil
Fil: Lalive, Arnaud L.. Universite de Lausanne; Suiza
dc.description.fil
Fil: Congiu, Mauro. Universite de Lausanne; Suiza
dc.description.fil
Fil: Gastaldo, Denise. Universite de Lausanne; Suiza
dc.description.fil
Fil: Tchenio, Anna. Universite de Lausanne; Suiza
dc.description.fil
Fil: Lecca, Salvatore. Universite de Lausanne; Suiza
dc.description.fil
Fil: Soiza Reilly, Mariano. Consejo Nacional de Investigaciones Científicas y Técnicas. Oficina de Coordinación Administrativa Ciudad Universitaria. Instituto de Fisiología, Biología Molecular y Neurociencias. Universidad de Buenos Aires. Facultad de Ciencias Exactas y Naturales. Instituto de Fisiología, Biología Molecular y Neurociencias; Argentina
dc.description.fil
Fil: Bagni, Claudia. Universite de Lausanne; Suiza
dc.description.fil
Fil: Mameli, Manuel. Inserm; Francia. Universite de Lausanne; Suiza
dc.journal.title
Neuron

dc.relation.alternativeid
info:eu-repo/semantics/altIdentifier/url/https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0896627321000088
dc.relation.alternativeid
info:eu-repo/semantics/altIdentifier/doi/http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2021.01.008
Archivos asociados