Artículo
Stress undermines reward-guided cognitive performance through synaptic depression in the lateral habenula
Nuno Perez, Alvaro; Trusel, Massimo; Lalive, Arnaud L.; Congiu, Mauro; Gastaldo, Denise; Tchenio, Anna; Lecca, Salvatore; Soiza Reilly, Mariano ; Bagni, Claudia; Mameli, Manuel
; Bagni, Claudia; Mameli, Manuel
 ; Bagni, Claudia; Mameli, Manuel
; Bagni, Claudia; Mameli, Manuel
Fecha de publicación:
03/2021
Editorial:
Cell Press
Revista:
Neuron
ISSN:
0896-6273
Idioma:
Inglés
Tipo de recurso:
Artículo publicado
Clasificación temática:
Resumen
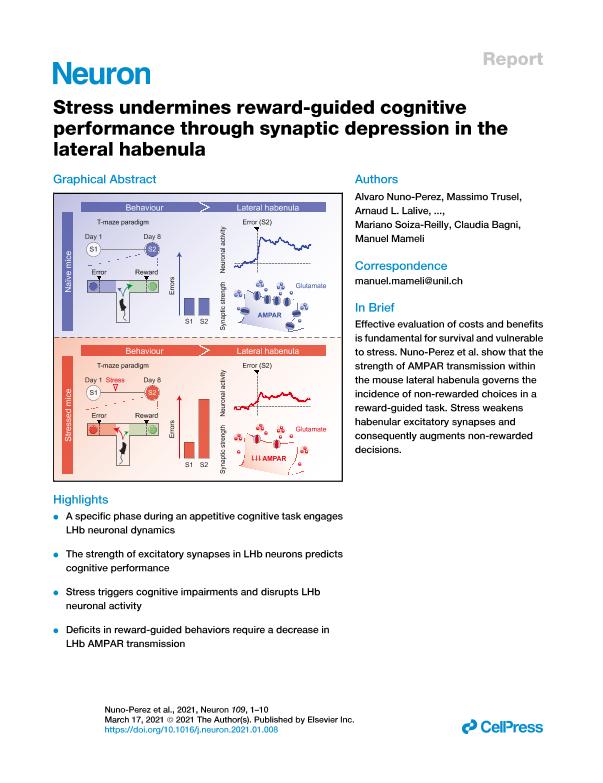
Weighing alternatives during reward pursuit is a vital cognitive computation that, when disrupted by stress, yields aspects of neuropsychiatric disorders. To examine the neural mechanisms underlying these phenomena, we employed a behavioral task in which mice were confronted by a reward and its omission (i.e., error). The experience of error outcomes engaged neuronal dynamics within the lateral habenula (LHb), a subcortical structure that supports appetitive behaviors and is susceptible to stress. A high incidence of errors predicted low strength of habenular excitatory synapses. Accordingly, stressful experiences increased error choices while decreasing glutamatergic neurotransmission onto LHb neurons. This synaptic adaptation required a reduction in postsynaptic AMPA receptors (AMPARs), irrespective of the anatomical source of glutamate. Bidirectional control of habenular AMPAR transmission recapitulated and averted stress-driven cognitive deficits. Thus, a subcortical synaptic mechanism vulnerable to stress underlies behavioral efficiency during cognitive performance.
Palabras clave:
AMPA RECEPTORS
,
LATERAL HABENULA
,
REWARD-GUIDED BEHAVIORS
,
STRESS
Archivos asociados
Licencia
Identificadores
Colecciones
Articulos(IFIBYNE)
Articulos de INST.DE FISIOL., BIOL.MOLECULAR Y NEUROCIENCIAS
Articulos de INST.DE FISIOL., BIOL.MOLECULAR Y NEUROCIENCIAS
Citación
Nuno Perez, Alvaro; Trusel, Massimo; Lalive, Arnaud L.; Congiu, Mauro; Gastaldo, Denise; et al.; Stress undermines reward-guided cognitive performance through synaptic depression in the lateral habenula; Cell Press; Neuron; 109; 6; 3-2021; 947-956
Compartir
Altmétricas