Mostrar el registro sencillo del ítem
dc.contributor.author
Lustemberg, Pablo German

dc.contributor.author
Bosco, Marta Verónica

dc.contributor.author
Bonivardi, Adrian Lionel

dc.contributor.author
Busnengo, Heriberto Fabio

dc.contributor.author
Ganduglia Pirovano, M. V.
dc.date.available
2016-12-19T18:16:09Z
dc.date.issued
2015-08
dc.identifier.citation
Lustemberg, Pablo German; Bosco, Marta Verónica; Bonivardi, Adrian Lionel; Busnengo, Heriberto Fabio; Ganduglia Pirovano, M. V.; Insights into the Nature of Formate Species in the Decomposition and Reaction of Methanol over Cerium Oxide Surfaces: A Combined Infrared Spectroscopy and Density Functional Theory Study; American Chemical Society; Journal Of Physical Chemistry C; 119; 37; 8-2015; 21452-21464
dc.identifier.issn
1932-7447
dc.identifier.uri
http://hdl.handle.net/11336/9734
dc.description.abstract
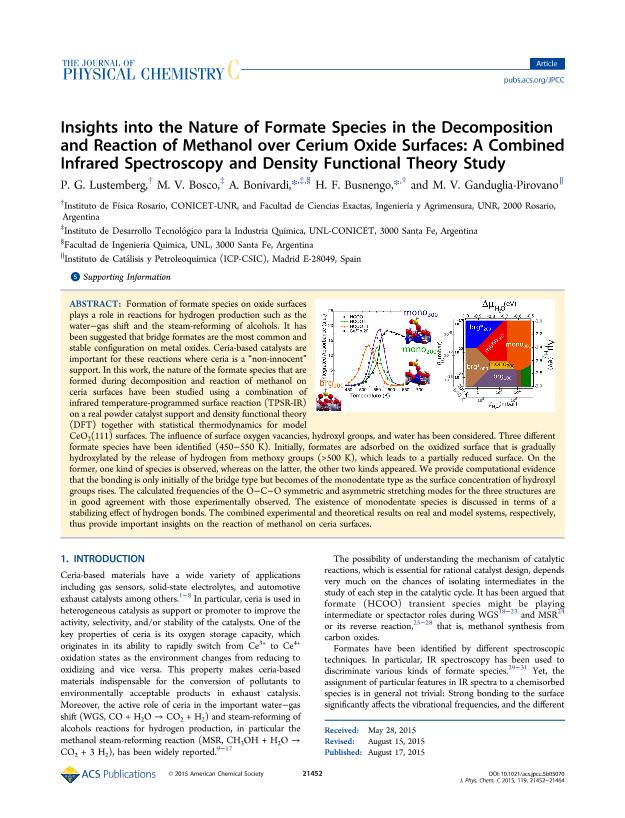
Formation of formate species on oxide surfaces plays a role in reactions for hydrogenproduction such as the water-gas shift, and the steam reforming of alcohols. It has beensuggested that bridge formates are the most common and stable configuration on metaloxides. Ceria-based catalysts are important for these reactions where ceria is a ?noninnocent?support. In this work, the nature of the formate species that are formedduring decomposition and reaction of methanol on ceria surfaces have been studiedusing a combination of infrared temperature programmed surface reaction (TPSR-IR)on a real powder catalyst support, and density functional theory (DFT) together withstatistical thermodynamics for model CeO2(111) surfaces. The influence of surfaceoxygen vacancies, hydroxyl groups, and water has been considered. Three differentformate species have been identified (450−550 K). Initially, formates are adsorbed onthe oxidized surface that is gradually hydroxylated by the release of hydrogen frommethoxy groups (> 500 K), which leads to a partially reduced surface. On the formerone kind of species is observed, whereas on the latter the other two kinds appeared. Weprovide computational evidence that the bonding is only initially of the bridge type, butbecomes of the monodentate type, as the surface concentration of hydroxyl groups rises.The calculated frequencies of the O−C−O symmetric and asymmetric stretching modesfor the three structures are in good agreement with those experimentally observed. Theexistence of monodentate species is discussed in terms of a stabilizing effect of hydrogenbonds. The combined experimental and theoretical results on real and model systems,respectively, thus provide important insights on the reaction of methanol on ceriasurfaces.
dc.format
application/pdf
dc.language.iso
eng
dc.publisher
American Chemical Society

dc.rights
info:eu-repo/semantics/openAccess
dc.rights.uri
https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/2.5/ar/
dc.subject
Formate Species
dc.subject
Co-Adsorbed Hydroxyl
dc.subject
Ir Spectroscopy
dc.subject
Density Functional Theory
dc.subject.classification
Física Atómica, Molecular y Química

dc.subject.classification
Ciencias Físicas

dc.subject.classification
CIENCIAS NATURALES Y EXACTAS

dc.title
Insights into the Nature of Formate Species in the Decomposition and Reaction of Methanol over Cerium Oxide Surfaces: A Combined Infrared Spectroscopy and Density Functional Theory Study
dc.type
info:eu-repo/semantics/article
dc.type
info:ar-repo/semantics/artículo
dc.type
info:eu-repo/semantics/publishedVersion
dc.date.updated
2016-12-16T15:04:02Z
dc.journal.volume
119
dc.journal.number
37
dc.journal.pagination
21452-21464
dc.journal.pais
Estados Unidos

dc.journal.ciudad
Washington
dc.description.fil
Fil: Lustemberg, Pablo German. Consejo Nacional de Investigaciones Científicas y Técnicas. Centro Científico Tecnológico Rosario. Instituto de Física de Rosario (i); Argentina
dc.description.fil
Fil: Bosco, Marta Verónica. Consejo Nacional de Investigaciones Científicas y Técnicas. Centro Científico Tecnológico Santa Fe. Instituto de Desarrollo Tecnológico Para la Industria Química (i); Argentina
dc.description.fil
Fil: Bonivardi, Adrian Lionel. Consejo Nacional de Investigaciones Científicas y Técnicas. Centro Científico Tecnológico Santa Fe. Instituto de Desarrollo Tecnológico Para la Industria Química (i); Argentina
dc.description.fil
Fil: Busnengo, Heriberto Fabio. Consejo Nacional de Investigaciones Científicas y Técnicas. Centro Científico Tecnológico Rosario. Instituto de Física de Rosario (i); Argentina
dc.description.fil
Fil: Ganduglia Pirovano, M. V.. Consejo Superior de Investigaciones Cientificas. Instituto de Catalisis y Petroleoquimica; España
dc.journal.title
Journal Of Physical Chemistry C

dc.relation.alternativeid
info:eu-repo/semantics/altIdentifier/url/http://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/acs.jpcc.5b05070
dc.relation.alternativeid
info:eu-repo/semantics/altIdentifier/doi/http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpcc.5b05070
Archivos asociados