Mostrar el registro sencillo del ítem
dc.contributor.author
Pickering, Ignacio
dc.contributor.author
Paleico, Martín Leandro

dc.contributor.author
Pérez Sirkin, Yamila Anahí

dc.contributor.author
Scherlis Perel, Damian Ariel

dc.contributor.author
Factorovich, Matias Hector

dc.date.available
2019-11-22T18:04:57Z
dc.date.issued
2018-05
dc.identifier.citation
Pickering, Ignacio; Paleico, Martín Leandro; Pérez Sirkin, Yamila Anahí; Scherlis Perel, Damian Ariel; Factorovich, Matias Hector; Grand Canonical Investigation of the Quasi Liquid Layer of Ice: Is It Liquid?; American Chemical Society; Journal of Physical Chemistry B; 122; 18; 5-2018; 4880-4890
dc.identifier.issn
1520-6106
dc.identifier.uri
http://hdl.handle.net/11336/89589
dc.description.abstract
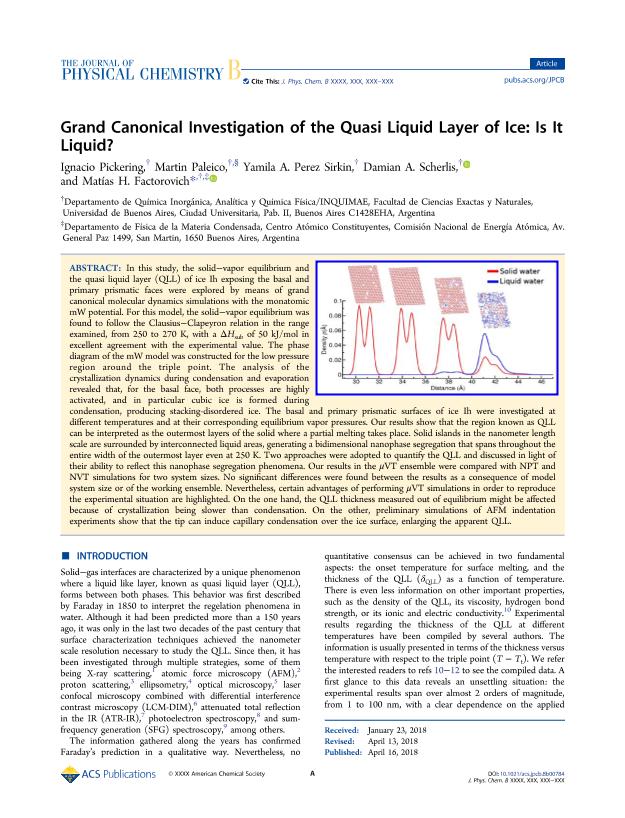
In this study, the solid-vapor equilibrium and the quasi liquid layer (QLL) of ice Ih exposing the basal and primary prismatic faces were explored by means of grand canonical molecular dynamics simulations with the monatomic mW potential. For this model, the solid-vapor equilibrium was found to follow the Clausius-Clapeyron relation in the range examined, from 250 to 270 K, with a δHsub of 50 kJ/mol in excellent agreement with the experimental value. The phase diagram of the mW model was constructed for the low pressure region around the triple point. The analysis of the crystallization dynamics during condensation and evaporation revealed that, for the basal face, both processes are highly activated, and in particular cubic ice is formed during condensation, producing stacking-disordered ice. The basal and primary prismatic surfaces of ice Ih were investigated at different temperatures and at their corresponding equilibrium vapor pressures. Our results show that the region known as QLL can be interpreted as the outermost layers of the solid where a partial melting takes place. Solid islands in the nanometer length scale are surrounded by interconnected liquid areas, generating a bidimensional nanophase segregation that spans throughout the entire width of the outermost layer even at 250 K. Two approaches were adopted to quantify the QLL and discussed in light of their ability to reflect this nanophase segregation phenomena. Our results in the μVT ensemble were compared with NPT and NVT simulations for two system sizes. No significant differences were found between the results as a consequence of model system size or of the working ensemble. Nevertheless, certain advantages of performing μVT simulations in order to reproduce the experimental situation are highlighted. On the one hand, the QLL thickness measured out of equilibrium might be affected because of crystallization being slower than condensation. On the other, preliminary simulations of AFM indentation experiments show that the tip can induce capillary condensation over the ice surface, enlarging the apparent QLL.
dc.format
application/pdf
dc.language.iso
eng
dc.publisher
American Chemical Society

dc.rights
info:eu-repo/semantics/openAccess
dc.rights.uri
https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/2.5/ar/
dc.subject
QLL
dc.subject.classification
Físico-Química, Ciencia de los Polímeros, Electroquímica

dc.subject.classification
Ciencias Químicas

dc.subject.classification
CIENCIAS NATURALES Y EXACTAS

dc.title
Grand Canonical Investigation of the Quasi Liquid Layer of Ice: Is It Liquid?
dc.type
info:eu-repo/semantics/article
dc.type
info:ar-repo/semantics/artículo
dc.type
info:eu-repo/semantics/publishedVersion
dc.date.updated
2019-10-16T15:24:23Z
dc.journal.volume
122
dc.journal.number
18
dc.journal.pagination
4880-4890
dc.journal.pais
Estados Unidos

dc.description.fil
Fil: Pickering, Ignacio. Consejo Nacional de Investigaciones Científicas y Técnicas. Oficina de Coordinación Administrativa Ciudad Universitaria. Instituto de Química, Física de los Materiales, Medioambiente y Energía. Universidad de Buenos Aires. Facultad de Ciencias Exactas y Naturales. Instituto de Química, Física de los Materiales, Medioambiente y Energía; Argentina
dc.description.fil
Fil: Paleico, Martín Leandro. Consejo Nacional de Investigaciones Científicas y Técnicas. Oficina de Coordinación Administrativa Ciudad Universitaria. Instituto de Química, Física de los Materiales, Medioambiente y Energía. Universidad de Buenos Aires. Facultad de Ciencias Exactas y Naturales. Instituto de Química, Física de los Materiales, Medioambiente y Energía; Argentina
dc.description.fil
Fil: Pérez Sirkin, Yamila Anahí. Consejo Nacional de Investigaciones Científicas y Técnicas. Oficina de Coordinación Administrativa Ciudad Universitaria. Instituto de Química, Física de los Materiales, Medioambiente y Energía. Universidad de Buenos Aires. Facultad de Ciencias Exactas y Naturales. Instituto de Química, Física de los Materiales, Medioambiente y Energía; Argentina
dc.description.fil
Fil: Scherlis Perel, Damian Ariel. Consejo Nacional de Investigaciones Científicas y Técnicas. Oficina de Coordinación Administrativa Ciudad Universitaria. Instituto de Química, Física de los Materiales, Medioambiente y Energía. Universidad de Buenos Aires. Facultad de Ciencias Exactas y Naturales. Instituto de Química, Física de los Materiales, Medioambiente y Energía; Argentina
dc.description.fil
Fil: Factorovich, Matias Hector. Consejo Nacional de Investigaciones Científicas y Técnicas. Oficina de Coordinación Administrativa Ciudad Universitaria. Instituto de Química, Física de los Materiales, Medioambiente y Energía. Universidad de Buenos Aires. Facultad de Ciencias Exactas y Naturales. Instituto de Química, Física de los Materiales, Medioambiente y Energía; Argentina. Comisión Nacional de Energía Atómica. Centro Atómico Constituyentes; Argentina
dc.journal.title
Journal of Physical Chemistry B

dc.relation.alternativeid
info:eu-repo/semantics/altIdentifier/url/https://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/acs.jpcb.8b00784
dc.relation.alternativeid
info:eu-repo/semantics/altIdentifier/doi/http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpcb.8b00784
Archivos asociados