Artículo
Diffusion of Water and Electrolytes in Mesoporous Silica with a Wide Range of Pore Sizes
Martínez Casillas, Diana Cristina ; Longinotti, María Paula
; Longinotti, María Paula ; Bruno, Mariano Martín
; Bruno, Mariano Martín ; Vaca Chávez Fornasero, Fabián
; Vaca Chávez Fornasero, Fabián ; Acosta, Rodolfo Héctor
; Acosta, Rodolfo Héctor ; Corti, Horacio Roberto
; Corti, Horacio Roberto
 ; Longinotti, María Paula
; Longinotti, María Paula ; Bruno, Mariano Martín
; Bruno, Mariano Martín ; Vaca Chávez Fornasero, Fabián
; Vaca Chávez Fornasero, Fabián ; Acosta, Rodolfo Héctor
; Acosta, Rodolfo Héctor ; Corti, Horacio Roberto
; Corti, Horacio Roberto
Fecha de publicación:
02/2018
Editorial:
American Chemical Society
Revista:
Journal of Physical Chemistry C
ISSN:
1932-7447
e-ISSN:
1932-7455
Idioma:
Inglés
Tipo de recurso:
Artículo publicado
Clasificación temática:
Resumen
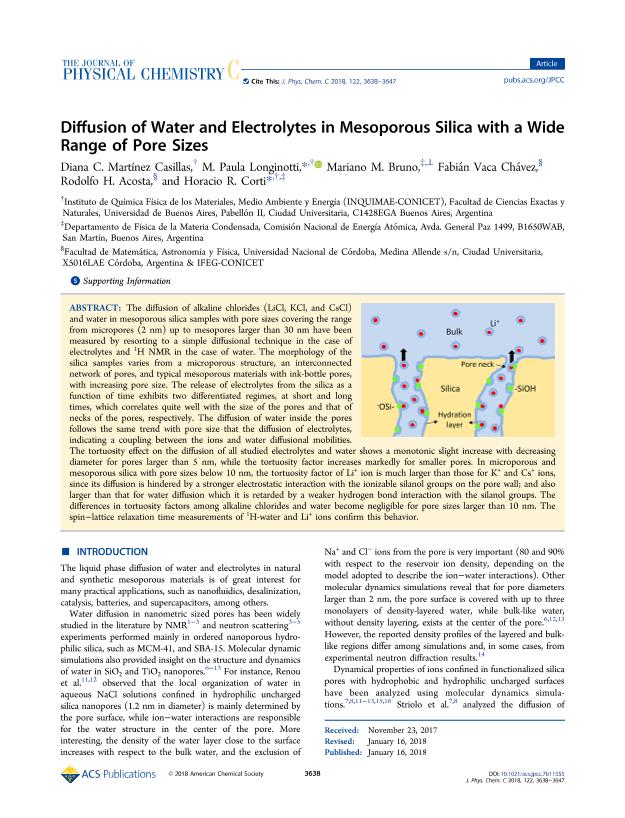
The diffusion of alkaline chlorides (LiCl, KCl, and CsCl) and water in mesoporous silica samples with pore sizes covering the range from micropores (2 nm) up to mesopores larger than 30 nm have been measured by resorting to a simple diffusional technique in the case of electrolytes and 1H NMR in the case of water. The morphology of the silica samples varies from a microporous structure, an interconnected network of pores, and typical mesoporous materials with ink-bottle pores, with increasing pore size. The release of electrolytes from the silica as a function of time exhibits two differentiated regimes, at short and long times, which correlates quite well with the size of the pores and that of necks of the pores, respectively. The diffusion of water inside the pores follows the same trend with pore size that the diffusion of electrolytes, indicating a coupling between the ions and water diffusional mobilities. The tortuosity effect on the diffusion of all studied electrolytes and water shows a monotonic slight increase with decreasing diameter for pores larger than 5 nm, while the tortuosity factor increases markedly for smaller pores. In microporous and mesoporous silica with pore sizes below 10 nm, the tortuosity factor of Li+ ion is much larger than those for K+ and Cs+ ions, since its diffusion is hindered by a stronger electrostatic interaction with the ionizable silanol groups on the pore wall; and also larger than that for water diffusion which it is retarded by a weaker hydrogen bond interaction with the silanol groups. The differences in tortuosity factors among alkaline chlorides and water become negligible for pore sizes larger than 10 nm. The spin-lattice relaxation time measurements of 1H-water and Li+ ions confirm this behavior.
Palabras clave:
Silica
,
Difusion
,
Litio
,
Agua
,
Litio
Archivos asociados
Licencia
Identificadores
Colecciones
Articulos(CCT - CORDOBA)
Articulos de CTRO.CIENTIFICO TECNOL.CONICET - CORDOBA
Articulos de CTRO.CIENTIFICO TECNOL.CONICET - CORDOBA
Articulos(IFEG)
Articulos de INST.DE FISICA ENRIQUE GAVIOLA
Articulos de INST.DE FISICA ENRIQUE GAVIOLA
Articulos(INQUIMAE)
Articulos de INST.D/QUIM FIS D/L MATERIALES MEDIOAMB Y ENERGIA
Articulos de INST.D/QUIM FIS D/L MATERIALES MEDIOAMB Y ENERGIA
Articulos(SEDE CENTRAL)
Articulos de SEDE CENTRAL
Articulos de SEDE CENTRAL
Citación
Martínez Casillas, Diana Cristina; Longinotti, María Paula; Bruno, Mariano Martín; Vaca Chávez Fornasero, Fabián; Acosta, Rodolfo Héctor; et al.; Diffusion of Water and Electrolytes in Mesoporous Silica with a Wide Range of Pore Sizes; American Chemical Society; Journal of Physical Chemistry C; 122; 6; 2-2018; 3638-3647
Compartir
Altmétricas