Mostrar el registro sencillo del ítem
dc.contributor.author
Agirre, Eneritz
dc.contributor.author
Bellora, Nicolás

dc.contributor.author
Alló, Mariano

dc.contributor.author
Pagès, Amadís
dc.contributor.author
Bertucci, Paola Yanina

dc.contributor.author
Kornblihtt, Alberto Rodolfo

dc.contributor.author
Eyras, Eduardo
dc.date.available
2019-10-10T17:28:24Z
dc.date.issued
2015-12-02
dc.identifier.citation
Agirre, Eneritz; Bellora, Nicolás; Alló, Mariano; Pagès, Amadís; Bertucci, Paola Yanina; et al.; A chromatin code for alternative splicing involving a putative association between CTCF and HP1aα proteins; BioMed Central; Bmc Biology; 13; 1; 2-12-2015; 1-14
dc.identifier.issn
1741-7007
dc.identifier.uri
http://hdl.handle.net/11336/85531
dc.description.abstract
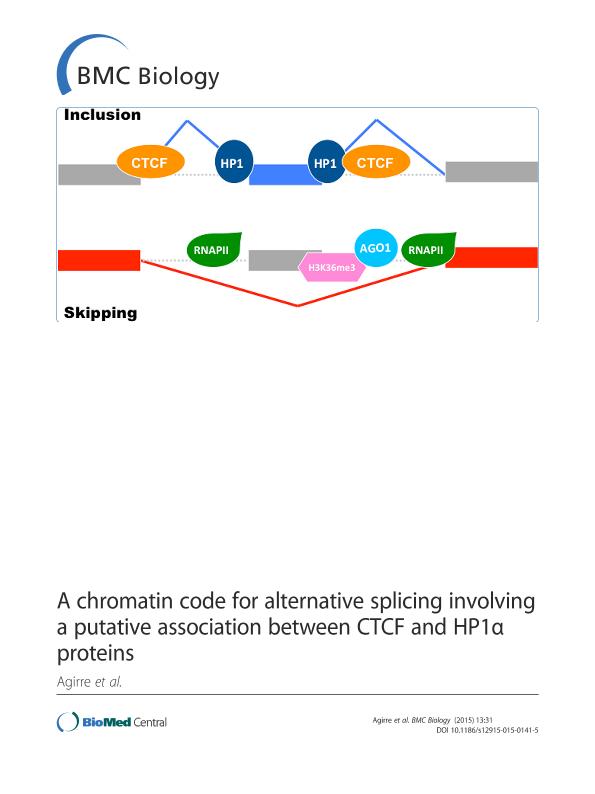
Background: Alternative splicing is primarily controlled by the activity of splicing factors and by the elongation of the RNA polymerase II (RNAPII). Recent experiments have suggested a new complex network of splicing regulation involving chromatin, transcription and multiple protein factors. In particular, the CCCTC-binding factor (CTCF), the Argonaute protein AGO1, and members of the heterochromatin protein 1 (HP1) family have been implicated in the regulation of splicing associated with chromatin and the elongation of RNAPII. These results raise the question of whether these proteins may associate at the chromatin level to modulate alternative splicing. Results: Using chromatin immunoprecipitation sequencing (ChIP-Seq) data for CTCF, AGO1, HP1aα, H3K27me3, H3K9me2, H3K36me3, RNAPII, total H3 and 5metC and alternative splicing arrays from two cell lines, we have analyzed the combinatorial code of their binding to chromatin in relation to the alternative splicing patterns between two cell lines, MCF7 and MCF10. Using Machine Learning techniques, we identified the changes in chromatin signals that are most significantly associated with splicing regulation between these two cell lines. Moreover, we have built a map of the chromatin signals on the pre-mRNA, that is, a chromatin-based RNA-map, which can explain 606 (68.55%) of the regulated events between MCF7 and MCF10. This chromatin code involves the presence of HP1aα, CTCF, AGO1, RNAPII and histone marks around regulated exons and can differentiate patterns of skipping and inclusion. Additionally, we found a significant association of HP1aα and CTCF activities around the regulated exons and a putative DNA binding site for HP1aα. Conclusions: Our results show that a considerable number of alternative splicing events could have a chromatin-dependent regulation involving the association of HP1aα and CTCF near regulated exons. Additionally, we find further evidence for the involvement of HP1aα and AGO1 in chromatin-related splicing regulation.
dc.format
application/pdf
dc.language.iso
eng
dc.publisher
BioMed Central

dc.rights
info:eu-repo/semantics/openAccess
dc.rights.uri
https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.5/ar/
dc.subject
CHROMATIN
dc.subject
HISTONES
dc.subject
SPLICING
dc.subject
SPLICING CODE
dc.subject.classification
Bioquímica y Biología Molecular

dc.subject.classification
Ciencias Biológicas

dc.subject.classification
CIENCIAS NATURALES Y EXACTAS

dc.title
A chromatin code for alternative splicing involving a putative association between CTCF and HP1aα proteins
dc.type
info:eu-repo/semantics/article
dc.type
info:ar-repo/semantics/artículo
dc.type
info:eu-repo/semantics/publishedVersion
dc.date.updated
2019-09-30T18:50:59Z
dc.journal.volume
13
dc.journal.number
1
dc.journal.pagination
1-14
dc.journal.pais
Reino Unido

dc.journal.ciudad
Londres
dc.description.fil
Fil: Agirre, Eneritz. Universitat Pompeu Fabra; España. Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique; Francia. Institute of Human Genetics; Francia
dc.description.fil
Fil: Bellora, Nicolás. Consejo Nacional de Investigaciones Científicas y Técnicas. Centro Científico Tecnológico Conicet - Patagonia Norte. Instituto de Investigaciones en Biodiversidad y Medioambiente. Universidad Nacional del Comahue. Centro Regional Universidad Bariloche. Instituto de Investigaciones en Biodiversidad y Medioambiente; Argentina. Universitat Pompeu Fabra; España
dc.description.fil
Fil: Alló, Mariano. Consejo Nacional de Investigaciones Científicas y Técnicas. Oficina de Coordinación Administrativa Ciudad Universitaria. Instituto de Fisiología, Biología Molecular y Neurociencias. Universidad de Buenos Aires. Facultad de Ciencias Exactas y Naturales. Instituto de Fisiología, Biología Molecular y Neurociencias; Argentina. European Molecular Biology Laboratory; Alemania
dc.description.fil
Fil: Pagès, Amadís. Universitat Pompeu Fabra; España
dc.description.fil
Fil: Bertucci, Paola Yanina. Consejo Nacional de Investigaciones Científicas y Técnicas. Oficina de Coordinación Administrativa Ciudad Universitaria. Instituto de Fisiología, Biología Molecular y Neurociencias. Universidad de Buenos Aires. Facultad de Ciencias Exactas y Naturales. Instituto de Fisiología, Biología Molecular y Neurociencias; Argentina. European Molecular Biology Laboratory; Alemania
dc.description.fil
Fil: Kornblihtt, Alberto Rodolfo. Consejo Nacional de Investigaciones Científicas y Técnicas. Oficina de Coordinación Administrativa Ciudad Universitaria. Instituto de Fisiología, Biología Molecular y Neurociencias. Universidad de Buenos Aires. Facultad de Ciencias Exactas y Naturales. Instituto de Fisiología, Biología Molecular y Neurociencias; Argentina
dc.description.fil
Fil: Eyras, Eduardo. Universitat Pompeu Fabra; España. Institució Catalana de Recerca i Estudis Avancats; España
dc.journal.title
Bmc Biology

dc.relation.alternativeid
info:eu-repo/semantics/altIdentifier/doi/http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/s12915-015-0141-5
dc.relation.alternativeid
info:eu-repo/semantics/altIdentifier/url/https://bmcbiol.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12915-015-0141-5
Archivos asociados