Artículo
Importance of the Hydration Degree in the Use of Clay-Fungal Biocomposites as Adsorbents for Uranium Uptake
Olivelli, Melisa Soledad ; Schampera, Birgit; Woche, Susanne K.; Torres Sanchez, Rosa Maria
; Schampera, Birgit; Woche, Susanne K.; Torres Sanchez, Rosa Maria ; Curutchet, Gustavo Andres
; Curutchet, Gustavo Andres
 ; Schampera, Birgit; Woche, Susanne K.; Torres Sanchez, Rosa Maria
; Schampera, Birgit; Woche, Susanne K.; Torres Sanchez, Rosa Maria ; Curutchet, Gustavo Andres
; Curutchet, Gustavo Andres
Fecha de publicación:
03/2017
Editorial:
American Chemical Society
Revista:
Industrial & Engineering Chemical Research
ISSN:
0888-5885
Idioma:
Inglés
Tipo de recurso:
Artículo publicado
Clasificación temática:
Resumen
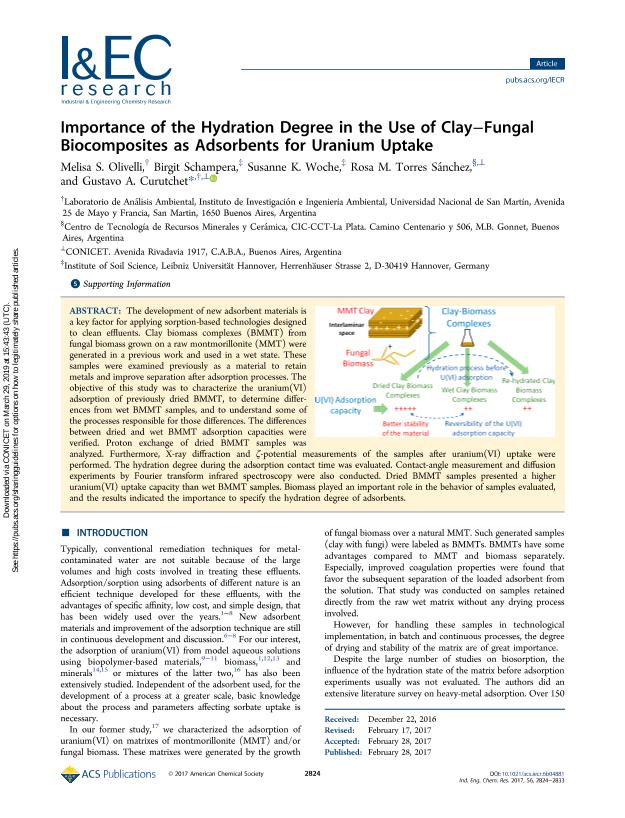
The development of new adsorbent materials is a key factor for applying sorption-based technologies designed to clean effluents. Clay biomass complexes (BMMT) from fungal biomass grown on a raw montmorillonite (MMT) were generated in a previous work and used in a wet state. These samples were examined previously as a material to retain metals and improve separation after adsorption processes. The objective of this study was to characterize the uranium(VI) adsorption of previously dried BMMT, to determine differences from wet BMMT samples, and to understand some of the processes responsible for those differences. The differences between dried and wet BMMT adsorption capacities were verified. Proton exchange of dried BMMT samples was analyzed. Furthermore, X-ray diffraction and ζ-potential measurements of the samples after uranium(VI) uptake were performed. The hydration degree during the adsorption contact time was evaluated. Contact-angle measurement and diffusion experiments by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy were also conducted. Dried BMMT samples presented a higher uranium(VI) uptake capacity than wet BMMT samples. Biomass played an important role in the behavior of samples evaluated, and the results indicated the importance to specify the hydration degree of adsorbents.
Palabras clave:
Uranium
,
Montmorillonite
,
Biosorption
Archivos asociados
Licencia
Identificadores
Colecciones
Articulos(CETMIC)
Articulos de CENTRO TECNOL.DE REC.MINERALES Y CERAMICA (I)
Articulos de CENTRO TECNOL.DE REC.MINERALES Y CERAMICA (I)
Articulos(SEDE CENTRAL)
Articulos de SEDE CENTRAL
Articulos de SEDE CENTRAL
Citación
Olivelli, Melisa Soledad; Schampera, Birgit; Woche, Susanne K.; Torres Sanchez, Rosa Maria; Curutchet, Gustavo Andres; Importance of the Hydration Degree in the Use of Clay-Fungal Biocomposites as Adsorbents for Uranium Uptake; American Chemical Society; Industrial & Engineering Chemical Research; 56; 10; 3-2017; 2824-2833
Compartir
Altmétricas