Mostrar el registro sencillo del ítem
dc.contributor.author
Jurss, Jonah W.
dc.contributor.author
Concepcion, Javier J.
dc.contributor.author
Butler, Jennifer M.
dc.contributor.author
Omberg, Kristin M.
dc.contributor.author
Baraldo Victorica, Luis Mario

dc.contributor.author
Thompson, Darla Graff
dc.contributor.author
Lebeau, Estelle L.
dc.contributor.author
Hornstein, Brooks
dc.contributor.author
Schoonover, Jon R.
dc.contributor.author
Jude, Hershel
dc.contributor.author
Thompson, Joe D.
dc.contributor.author
Dattelbaum, Dana M.
dc.contributor.author
Rocha, Reginaldo C.
dc.contributor.author
Templeton, Joseph L.
dc.contributor.author
Meyer, Thomas J.
dc.date.available
2019-02-05T21:12:20Z
dc.date.issued
2012-02
dc.identifier.citation
Jurss, Jonah W.; Concepcion, Javier J.; Butler, Jennifer M.; Omberg, Kristin M.; Baraldo Victorica, Luis Mario; et al.; Electronic structure of the water oxidation catalyst cis, cis -[(bpy) 2(H 2O)Ru IIIORu III(OH 2)(bpy) 2] 4+, the blue dimer; American Chemical Society; Inorganic Chemistry; 51; 3; 2-2012; 1345-1358
dc.identifier.issn
0020-1669
dc.identifier.uri
http://hdl.handle.net/11336/69484
dc.description.abstract
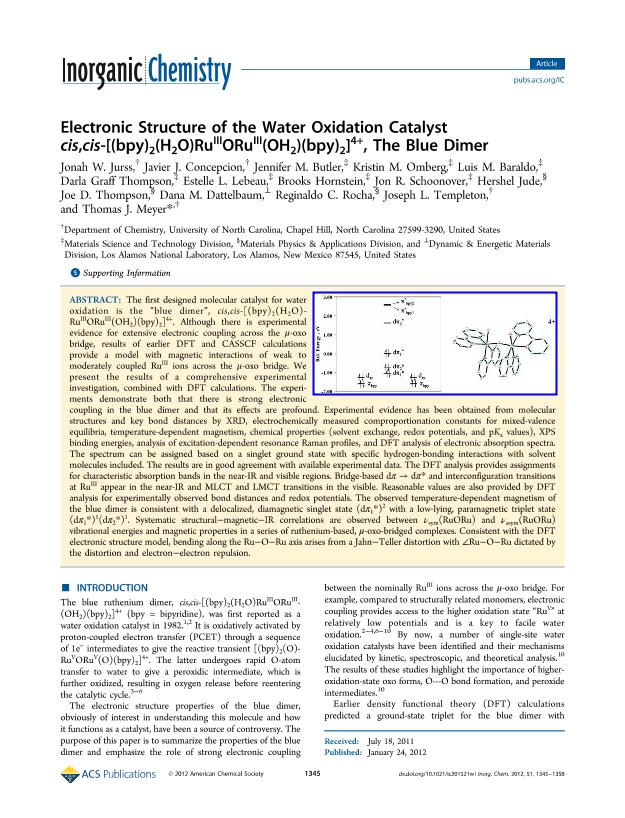
The first designed molecular catalyst for water oxidation is the "blue dimer", cis,cis-[(bpy) 2(H 2O)Ru IIIORu III(OH 2)(bpy) 2] 4+. Although there is experimental evidence for extensive electronic coupling across the μ-oxo bridge, results of earlier DFT and CASSCF calculations provide a model with magnetic interactions of weak to moderately coupled Ru III ions across the μ-oxo bridge. We present the results of a comprehensive experimental investigation, combined with DFT calculations. The experiments demonstrate both that there is strong electronic coupling in the blue dimer and that its effects are profound. Experimental evidence has been obtained from molecular structures and key bond distances by XRD, electrochemically measured comproportionation constants for mixed-valence equilibria, temperature-dependent magnetism, chemical properties (solvent exchange, redox potentials, and pK a values), XPS binding energies, analysis of excitation-dependent resonance Raman profiles, and DFT analysis of electronic absorption spectra. The spectrum can be assigned based on a singlet ground state with specific hydrogen-bonding interactions with solvent molecules included. The results are in good agreement with available experimental data. The DFT analysis provides assignments for characteristic absorption bands in the near-IR and visible regions. Bridge-based dπ → dπ* and interconfiguration transitions at Ru III appear in the near-IR and MLCT and LMCT transitions in the visible. Reasonable values are also provided by DFT analysis for experimentally observed bond distances and redox potentials. The observed temperature-dependent magnetism of the blue dimer is consistent with a delocalized, diamagnetic singlet state (dπ 1*) 2 with a low-lying, paramagnetic triplet state (dπ 1*) 1(dπ 2*) 1. Systematic structural-magnetic-IR correlations are observed between ν sym(RuORu) and ν asym(RuORu) vibrational energies and magnetic properties in a series of ruthenium-based, μ-oxo-bridged complexes. Consistent with the DFT electronic structure model, bending along the Ru-O-Ru axis arises from a Jahn-Teller distortion with Ru-O-Ru dictated by the distortion and electron-electron repulsion. © 2012 American Chemical Society.
dc.format
application/pdf
dc.language.iso
eng
dc.publisher
American Chemical Society

dc.rights
info:eu-repo/semantics/openAccess
dc.rights.uri
https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/2.5/ar/
dc.subject
Catalysis
dc.subject
Reaction Kinetics
dc.subject
Inorganic Reaction Mechanisms
dc.subject.classification
Otras Ciencias Químicas

dc.subject.classification
Ciencias Químicas

dc.subject.classification
CIENCIAS NATURALES Y EXACTAS

dc.title
Electronic structure of the water oxidation catalyst cis, cis -[(bpy) 2(H 2O)Ru IIIORu III(OH 2)(bpy) 2] 4+, the blue dimer
dc.type
info:eu-repo/semantics/article
dc.type
info:ar-repo/semantics/artículo
dc.type
info:eu-repo/semantics/publishedVersion
dc.date.updated
2019-01-09T14:22:10Z
dc.journal.volume
51
dc.journal.number
3
dc.journal.pagination
1345-1358
dc.journal.pais
Estados Unidos

dc.journal.ciudad
Washington
dc.description.fil
Fil: Jurss, Jonah W.. University of North Carolina; Estados Unidos
dc.description.fil
Fil: Concepcion, Javier J.. University of North Carolina; Estados Unidos
dc.description.fil
Fil: Butler, Jennifer M.. Los Alamos National Laboratory; Estados Unidos
dc.description.fil
Fil: Omberg, Kristin M.. Los Alamos National Laboratory; Estados Unidos
dc.description.fil
Fil: Baraldo Victorica, Luis Mario. Consejo Nacional de Investigaciones Científicas y Técnicas; Argentina. Los Alamos National Laboratory; Estados Unidos
dc.description.fil
Fil: Thompson, Darla Graff. Los Alamos National Laboratory; Estados Unidos
dc.description.fil
Fil: Lebeau, Estelle L.. Los Alamos National Laboratory; Estados Unidos
dc.description.fil
Fil: Hornstein, Brooks. Los Alamos National Laboratory; Estados Unidos
dc.description.fil
Fil: Schoonover, Jon R.. Los Alamos National Laboratory; Estados Unidos
dc.description.fil
Fil: Jude, Hershel. Los Alamos National Laboratory; Estados Unidos
dc.description.fil
Fil: Thompson, Joe D.. Los Alamos National Laboratory; Estados Unidos
dc.description.fil
Fil: Dattelbaum, Dana M.. Los Alamos National Laboratory; Estados Unidos
dc.description.fil
Fil: Rocha, Reginaldo C.. Los Alamos National Laboratory; Estados Unidos
dc.description.fil
Fil: Templeton, Joseph L.. University of North Carolina; Estados Unidos
dc.description.fil
Fil: Meyer, Thomas J.. University of North Carolina; Estados Unidos
dc.journal.title
Inorganic Chemistry

dc.relation.alternativeid
info:eu-repo/semantics/altIdentifier/doi/https://dx.doi.org/10.1021/ic201521w
dc.relation.alternativeid
info:eu-repo/semantics/altIdentifier/url/https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/ic201521w
Archivos asociados