Mostrar el registro sencillo del ítem
dc.contributor.author
Devard, Alejandra Veronica

dc.contributor.author
Pujro Tarquino, Richard Alfonzo

dc.contributor.author
de la Puente, Gabriela

dc.contributor.author
Sedran, Ulises Anselmo

dc.date.available
2018-07-17T14:21:38Z
dc.date.issued
2012-07
dc.identifier.citation
Devard, Alejandra Veronica; Pujro Tarquino, Richard Alfonzo; de la Puente, Gabriela; Sedran, Ulises Anselmo; Hydrocarbon Yield Structure in the Conversion of Heavy Model Molecules (Quinolin-65) on Fluidized Catalytic Cracking Catalyst; American Chemical Society; Energy & Fuels (print); 26; 7-2012; 5015-5019
dc.identifier.issn
0887-0624
dc.identifier.uri
http://hdl.handle.net/11336/52358
dc.description.abstract
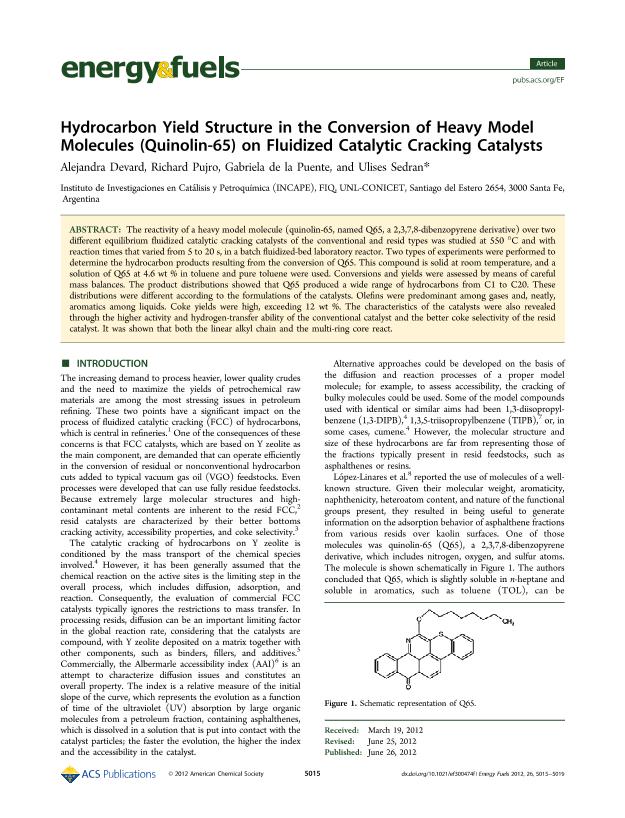
The reactivity of a heavy model molecule (quinolin-65, named Q65, a 2,3,7,8-dibenzopyrene derivative) over two different equilibrium fluidized catalytic cracking catalysts of the conventional and resid types was studied at 550 °C and with reaction times that varied from 5 to 20 s, in a batch fluidized-bed laboratory reactor. Two types of experiments were performed to determine the hydrocarbon products resulting from the conversion of Q65. This compound is solid at room temperature, and a solution of Q65 at 4.6 wt % in toluene and pure toluene were used. Conversions and yields were assessed by means of careful mass balances. The product distributions showed that Q65 produced a wide range of hydrocarbons from C1 to C20. These distributions were different according to the formulations of the catalysts. Olefins were predominant among gases and, neatly, aromatics among liquids. Coke yields were high, exceeding 12 wt %. The characteristics of the catalysts were also revealed through the higher activity and hydrogen-transfer ability of the conventional catalyst and the better coke selectivity of the resid catalyst. It was shown that both the linear alkyl chain and the multi-ring core react.
dc.format
application/pdf
dc.language.iso
eng
dc.publisher
American Chemical Society

dc.rights
info:eu-repo/semantics/openAccess
dc.rights.uri
https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/2.5/ar/
dc.subject
Fcc
dc.subject
Resids
dc.subject
Q65
dc.subject
Fuels
dc.subject.classification
Otras Ingeniería Química

dc.subject.classification
Ingeniería Química

dc.subject.classification
INGENIERÍAS Y TECNOLOGÍAS

dc.title
Hydrocarbon Yield Structure in the Conversion of Heavy Model Molecules (Quinolin-65) on Fluidized Catalytic Cracking Catalyst
dc.type
info:eu-repo/semantics/article
dc.type
info:ar-repo/semantics/artículo
dc.type
info:eu-repo/semantics/publishedVersion
dc.date.updated
2018-07-11T14:09:54Z
dc.journal.volume
26
dc.journal.pagination
5015-5019
dc.journal.pais
Estados Unidos

dc.journal.ciudad
Washington
dc.description.fil
Fil: Devard, Alejandra Veronica. Consejo Nacional de Investigaciones Científicas y Técnicas. Centro Científico Tecnológico Conicet - Santa Fe. Instituto de Investigaciones en Catálisis y Petroquímica ; Argentina
dc.description.fil
Fil: Pujro Tarquino, Richard Alfonzo. Consejo Nacional de Investigaciones Científicas y Técnicas. Centro Científico Tecnológico Conicet - Santa Fe. Instituto de Investigaciones en Catálisis y Petroquímica ; Argentina
dc.description.fil
Fil: de la Puente, Gabriela. Consejo Nacional de Investigaciones Científicas y Técnicas. Centro Científico Tecnológico Conicet - Santa Fe. Instituto de Investigaciones en Catálisis y Petroquímica ; Argentina
dc.description.fil
Fil: Sedran, Ulises Anselmo. Consejo Nacional de Investigaciones Científicas y Técnicas. Centro Científico Tecnológico Conicet - Santa Fe. Instituto de Investigaciones en Catálisis y Petroquímica ; Argentina
dc.journal.title
Energy & Fuels (print)

dc.relation.alternativeid
info:eu-repo/semantics/altIdentifier/url/http://pubs.acs.org/journal/enfuem
dc.relation.alternativeid
info:eu-repo/semantics/altIdentifier/doi/http://dx.doi.org//10.1021/ef300474f
Archivos asociados