Mostrar el registro sencillo del ítem
dc.contributor.author
Fonseca Ornelas, Luis
dc.contributor.author
Schmidt, Carla
dc.contributor.author
Camacho Zarco, Aldo R.
dc.contributor.author
Fernandez, Claudio Oscar

dc.contributor.author
Becker, Stefan
dc.contributor.author
Zweckstetter, Markus
dc.date.available
2018-06-28T19:01:48Z
dc.date.issued
2017-09
dc.identifier.citation
Fonseca Ornelas, Luis; Schmidt, Carla; Camacho Zarco, Aldo R.; Fernandez, Claudio Oscar; Becker, Stefan; et al.; Small-Molecule-Induced Soluble Oligomers of α-Synuclein with Helical Structure; Wiley VCH Verlag; Chemistry- A European Journal; 23; 53; 9-2017; 13010-13014
dc.identifier.issn
0947-6539
dc.identifier.uri
http://hdl.handle.net/11336/50465
dc.description.abstract
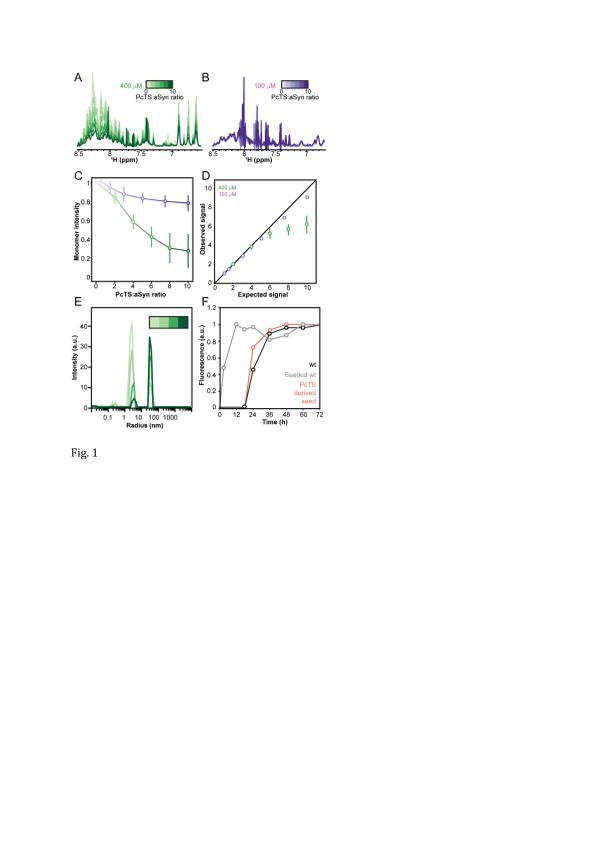
Accumulation of α-synuclein (αSyn) aggregates constitutes the hallmark of synucleinopathies including Parkinson's disease. However, many steps from the innocuous, monomeric αSyn toward misfolded oligomers and fibrillar species remain unclear. Here, we show that αSyn can form in solution α-helical oligomers, which are off-pathway to fibrillization, through interaction with the tetrapyrrole phthalocyanine tetrasulfonate. Chemical cross-linking combined with mass spectrometry reveals a large number of intermolecular cross-links along the entire αSyn sequence in the phthalocyanine tetrasulfonate-stabilized αSyn oligomers. Our study suggests that stabilization of structured oligomers by small molecules provides a viable strategy to interfere with αSyn fibrillization.
dc.format
application/pdf
dc.language.iso
eng
dc.publisher
Wiley VCH Verlag

dc.rights
info:eu-repo/semantics/openAccess
dc.rights.uri
https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/2.5/ar/
dc.subject
Alpha-Synuclein
dc.subject
Mass Spectrometry
dc.subject
Oligomers
dc.subject
Polymerization
dc.subject
Proteins
dc.subject.classification
Otras Ciencias Biológicas

dc.subject.classification
Ciencias Biológicas

dc.subject.classification
CIENCIAS NATURALES Y EXACTAS

dc.title
Small-Molecule-Induced Soluble Oligomers of α-Synuclein with Helical Structure
dc.type
info:eu-repo/semantics/article
dc.type
info:ar-repo/semantics/artículo
dc.type
info:eu-repo/semantics/publishedVersion
dc.date.updated
2018-06-28T14:15:01Z
dc.journal.volume
23
dc.journal.number
53
dc.journal.pagination
13010-13014
dc.journal.pais
Alemania

dc.journal.ciudad
Weinheim
dc.description.fil
Fil: Fonseca Ornelas, Luis. Max Planck Institute for Biophysical Chemistry; Alemania
dc.description.fil
Fil: Schmidt, Carla. Martin Luther University Halle-Wittenberg; Alemania
dc.description.fil
Fil: Camacho Zarco, Aldo R.. German Center for Neurodegenerative Diseases ; Alemania
dc.description.fil
Fil: Fernandez, Claudio Oscar. Consejo Nacional de Investigaciones Científicas y Técnicas. Centro Científico Tecnológico Conicet - Rosario. Instituto de Investigaciones para el Descubrimiento de Fármacos de Rosario. Universidad Nacional de Rosario. Instituto de Investigaciones para el Descubrimiento de Fármacos de Rosario; Argentina. Max Planck Institute for Biophysical Chemistry; Alemania
dc.description.fil
Fil: Becker, Stefan. Max Planck Institute for Biophysical Chemistry; Alemania
dc.description.fil
Fil: Zweckstetter, Markus. Max Planck Institute for Biophysical Chemistry; Alemania. German Center for Neurodegenerative Diseases ; Alemania. Universität Göttingen; Alemania
dc.journal.title
Chemistry- A European Journal

dc.relation.alternativeid
info:eu-repo/semantics/altIdentifier/doi/https://dx.doi.org/10.1002/chem.201703001
dc.relation.alternativeid
info:eu-repo/semantics/altIdentifier/url/https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/chem.201703001
Archivos asociados