Mostrar el registro sencillo del ítem
dc.contributor.author
Hoijemberg, Pablo Ariel

dc.contributor.author
Pelczer, István
dc.date.available
2018-06-28T14:08:19Z
dc.date.issued
2018-01
dc.identifier.citation
Hoijemberg, Pablo Ariel; Pelczer, István; Fast Metabolite Identification in Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Metabolomic Studies: Statistical Peak Sorting and Peak Overlap Detection for More Reliable Database Queries; American Chemical Society; Journal of Proteome Research; 17; 1; 1-2018; 392-401
dc.identifier.issn
1535-3893
dc.identifier.uri
http://hdl.handle.net/11336/50325
dc.description.abstract
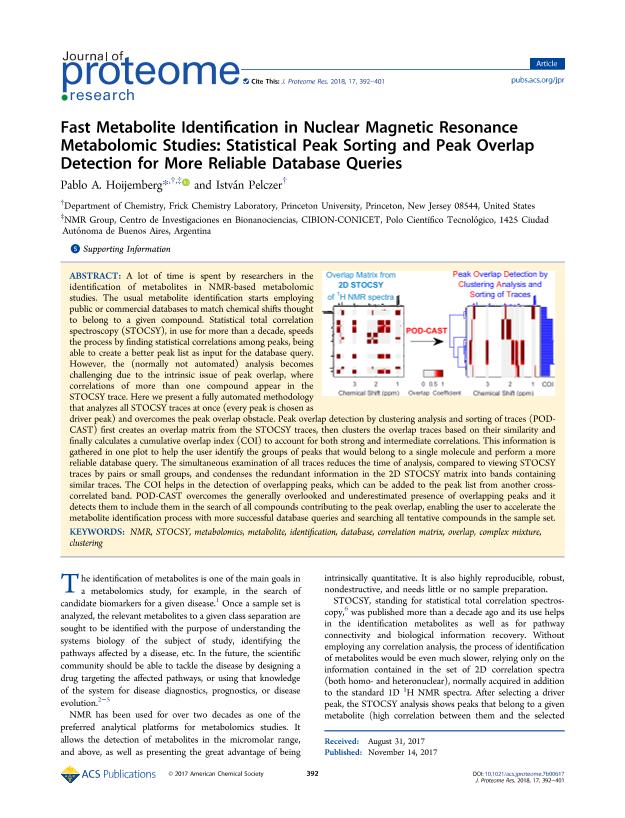
A lot of time is spent by researchers in the identification of metabolites in NMR-based metabolomic studies. The usual metabolite identification starts employing public or commercial databases to match chemical shifts thought to belong to a given compound. Statistical total correlation spectroscopy (STOCSY), in use for more than a decade, speeds the process by finding statistical correlations among peaks, being able to create a better peak list as input for the database query. However, the (normally not automated) analysis becomes challenging due to the intrinsic issue of peak overlap, where correlations of more than one compound appear in the STOCSY trace. Here we present a fully automated methodology that analyzes all STOCSY traces at once (every peak is chosen as driver peak) and overcomes the peak overlap obstacle. Peak overlap detection by clustering analysis and sorting of traces (POD-CAST) first creates an overlap matrix from the STOCSY traces, then clusters the overlap traces based on their similarity and finally calculates a cumulative overlap index (COI) to account for both strong and intermediate correlations. This information is gathered in one plot to help the user identify the groups of peaks that would belong to a single molecule and perform a more reliable database query. The simultaneous examination of all traces reduces the time of analysis, compared to viewing STOCSY traces by pairs or small groups, and condenses the redundant information in the 2D STOCSY matrix into bands containing similar traces. The COI helps in the detection of overlapping peaks, which can be added to the peak list from another cross-correlated band. POD-CAST overcomes the generally overlooked and underestimated presence of overlapping peaks and it detects them to include them in the search of all compounds contributing to the peak overlap, enabling the user to accelerate the metabolite identification process with more successful database queries and searching all tentative compounds in the sample set.
dc.format
application/pdf
dc.language.iso
eng
dc.publisher
American Chemical Society

dc.rights
info:eu-repo/semantics/openAccess
dc.rights.uri
https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/2.5/ar/
dc.subject
Clustering
dc.subject
Complex Mixture
dc.subject
Correlation Matrix
dc.subject
Database
dc.subject
Identification
dc.subject
Metabolite
dc.subject
Metabolomics
dc.subject
Nmr
dc.subject
Overlap
dc.subject
Stocsy
dc.subject.classification
Otras Ciencias Químicas

dc.subject.classification
Ciencias Químicas

dc.subject.classification
CIENCIAS NATURALES Y EXACTAS

dc.title
Fast Metabolite Identification in Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Metabolomic Studies: Statistical Peak Sorting and Peak Overlap Detection for More Reliable Database Queries
dc.type
info:eu-repo/semantics/article
dc.type
info:ar-repo/semantics/artículo
dc.type
info:eu-repo/semantics/publishedVersion
dc.date.updated
2018-06-22T14:42:49Z
dc.journal.volume
17
dc.journal.number
1
dc.journal.pagination
392-401
dc.journal.pais
Estados Unidos

dc.journal.ciudad
Maryland
dc.description.fil
Fil: Hoijemberg, Pablo Ariel. Consejo Nacional de Investigaciones Científicas y Técnicas. Oficina de Coordinación Administrativa Parque Centenario. Centro de Investigaciones en Bionanociencias "Elizabeth Jares Erijman"; Argentina. University of Princeton; Estados Unidos
dc.description.fil
Fil: Pelczer, István. University of Princeton; Estados Unidos
dc.journal.title
Journal of Proteome Research

dc.relation.alternativeid
info:eu-repo/semantics/altIdentifier/url/https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acs.jproteome.7b00617
dc.relation.alternativeid
info:eu-repo/semantics/altIdentifier/doi/http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/acs.jproteome.7b00617
Archivos asociados