Artículo
High Plasticity of New Granule Cells in the Aging Hippocampus
Trinchero, Mariela Fernanda ; Buttner, Karina A.; Sulkes Cuevas, Jessica N.; Temprana, Silvio Gabriel
; Buttner, Karina A.; Sulkes Cuevas, Jessica N.; Temprana, Silvio Gabriel ; Fontanet, Paula
; Fontanet, Paula ; Monzon Salinas, Maria Cristina; Ledda, Maria Fernanda
; Monzon Salinas, Maria Cristina; Ledda, Maria Fernanda ; Paratcha, Gustavo
; Paratcha, Gustavo ; Schinder, Alejandro Fabián
; Schinder, Alejandro Fabián
 ; Buttner, Karina A.; Sulkes Cuevas, Jessica N.; Temprana, Silvio Gabriel
; Buttner, Karina A.; Sulkes Cuevas, Jessica N.; Temprana, Silvio Gabriel ; Fontanet, Paula
; Fontanet, Paula ; Monzon Salinas, Maria Cristina; Ledda, Maria Fernanda
; Monzon Salinas, Maria Cristina; Ledda, Maria Fernanda ; Paratcha, Gustavo
; Paratcha, Gustavo ; Schinder, Alejandro Fabián
; Schinder, Alejandro Fabián
Fecha de publicación:
10/2017
Editorial:
Elsevier Science
Revista:
Cell Reports
ISSN:
2211-1247
Idioma:
Inglés
Tipo de recurso:
Artículo publicado
Clasificación temática:
Resumen
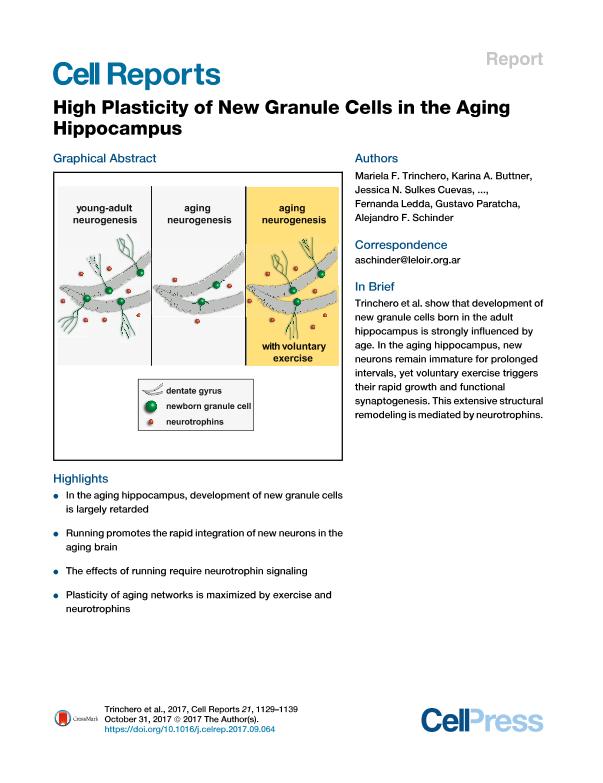
During aging, the brain undergoes changes that impair cognitive capacity and circuit plasticity, including a marked decrease in production of adult-born hippocampal neurons. It is unclear whether development and integration of those new neurons are also affected by age. Here, we show that adult-born granule cells (GCs) in aging mice are scarce and exhibit slow development, but they display a remarkable potential for structural plasticity. Retrovirally labeled 3-week-old GCs in middle-aged mice were small, underdeveloped, and disconnected. Neuronal development and integration were accelerated by voluntary exercise or environmental enrichment. Similar effects were observed via knockdown of Lrig1, an endogenous negative modulator of neurotrophin receptors. Consistently, blocking neurotrophin signaling by Lrig1 overexpression abolished the positive effects of exercise. These results demonstrate an unparalleled degree of plasticity in the aging brain mediated by neurotrophins, whereby new GCs remain immature until becoming rapidly recruited to the network by activity. Trinchero et al. show that development of new granule cells born in the adult hippocampus is strongly influenced by age. In the aging hippocampus, new neurons remain immature for prolonged intervals, yet voluntary exercise triggers their rapid growth and functional synaptogenesis. This extensive structural remodeling is mediated by neurotrophins.
Archivos asociados
Licencia
Identificadores
Colecciones
Articulos(IBCN)
Articulos de INST.DE BIOLO.CEL.Y NEURCS."PROF.E.DE ROBERTIS"
Articulos de INST.DE BIOLO.CEL.Y NEURCS."PROF.E.DE ROBERTIS"
Articulos(SEDE CENTRAL)
Articulos de SEDE CENTRAL
Articulos de SEDE CENTRAL
Citación
Trinchero, Mariela Fernanda; Buttner, Karina A.; Sulkes Cuevas, Jessica N.; Temprana, Silvio Gabriel; Fontanet, Paula; et al.; High Plasticity of New Granule Cells in the Aging Hippocampus; Elsevier Science; Cell Reports; 21; 5; 10-2017; 1129-1139
Compartir
Altmétricas