Mostrar el registro sencillo del ítem
dc.contributor.author
Fraire, Juan Carlos

dc.contributor.author
Sueldo Occello, Valeria Noemi

dc.contributor.author
Allende, Leandro German

dc.contributor.author
Veglia, Alicia Viviana

dc.contributor.author
Coronado, Eduardo A.

dc.date.available
2018-03-12T18:25:48Z
dc.date.issued
2015-04
dc.identifier.citation
Fraire, Juan Carlos; Sueldo Occello, Valeria Noemi; Allende, Leandro German; Veglia, Alicia Viviana; Coronado, Eduardo A.; Toward the design of highly stable small colloidal SERS substrates with supramolecular host-guest interactions for ultrasensitive detection; American Chemical Society; Journal of Physical Chemistry C; 119; 16; 4-2015; 8876-8888
dc.identifier.issn
1932-7447
dc.identifier.uri
http://hdl.handle.net/11336/38545
dc.description.abstract
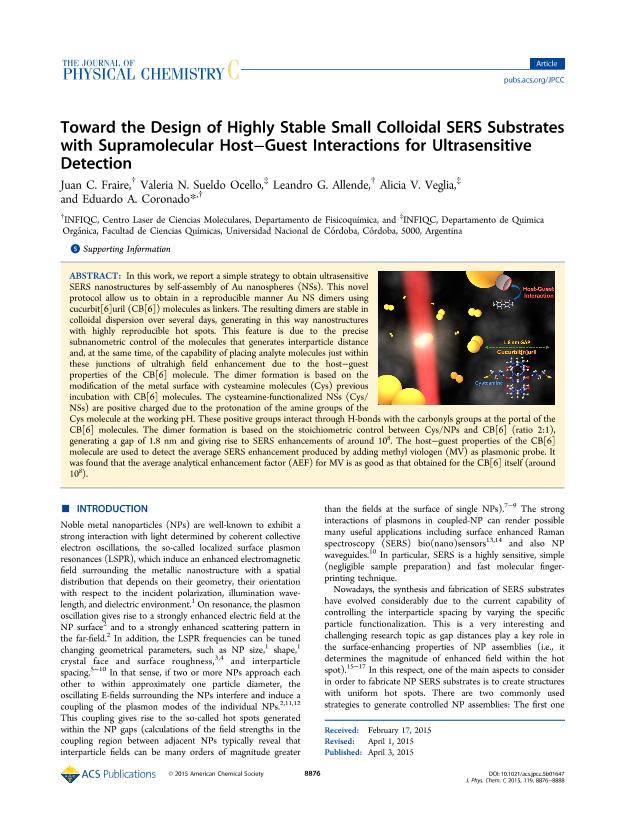
In this work, we report a simple strategy to obtain ultrasensitive SERS nanostructures by self-assembly of Au nanospheres (NSs). This novel protocol allow us to obtain in a reproducible manner Au NS dimers using cucurbit[6]uril (CB[6]) molecules as linkers. The resulting dimers are stable in colloidal dispersion over several days, generating in this way nanostructures with highly reproducible hot spots. This feature is due to the precise subnanometric control of the molecules that generates interparticle distance and, at the same time, of the capability of placing analyte molecules just within these junctions of ultrahigh field enhancement due to the host-guest properties of the CB[6] molecule. The dimer formation is based on the modification of the metal surface with cysteamine molecules (Cys) previous incubation with CB[6] molecules. The cysteamine-functionalized NSs (Cys/NSs) are positive charged due to the protonation of the amine groups of the Cys molecule at the working pH. These positive groups interact through H-bonds with the carbonyls groups at the portal of the CB[6] molecules. The dimer formation is based on the stoichiometric control between Cys/NPs and CB[6] (ratio 2:1), generating a gap of 1.8 nm and giving rise to SERS enhancements of around 108. The host-guest properties of the CB[6] molecule are used to detect the average SERS enhancement produced by adding methyl viologen (MV) as plasmonic probe. It was found that the average analytical enhancement factor (AEF) for MV is as good as that obtained for the CB[6] itself (around 108).
dc.format
application/pdf
dc.language.iso
eng
dc.publisher
American Chemical Society

dc.rights
info:eu-repo/semantics/openAccess
dc.rights.uri
https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/2.5/ar/
dc.subject
Colloidal
dc.subject
Sers
dc.subject
Supramolecular
dc.subject
Ultrasensitive
dc.subject.classification
Otras Ciencias Químicas

dc.subject.classification
Ciencias Químicas

dc.subject.classification
CIENCIAS NATURALES Y EXACTAS

dc.title
Toward the design of highly stable small colloidal SERS substrates with supramolecular host-guest interactions for ultrasensitive detection
dc.type
info:eu-repo/semantics/article
dc.type
info:ar-repo/semantics/artículo
dc.type
info:eu-repo/semantics/publishedVersion
dc.date.updated
2018-03-05T20:42:48Z
dc.journal.volume
119
dc.journal.number
16
dc.journal.pagination
8876-8888
dc.journal.pais
Estados Unidos

dc.description.fil
Fil: Fraire, Juan Carlos. Consejo Nacional de Investigaciones Científicas y Técnicas. Centro Científico Tecnológico Conicet - Córdoba. Instituto de Investigaciones en Físico-química de Córdoba. Universidad Nacional de Córdoba. Facultad de Ciencias Químicas. Instituto de Investigaciones en Físico-química de Córdoba; Argentina
dc.description.fil
Fil: Sueldo Occello, Valeria Noemi. Consejo Nacional de Investigaciones Científicas y Técnicas. Centro Científico Tecnológico Conicet - Córdoba. Instituto de Investigaciones en Físico-química de Córdoba. Universidad Nacional de Córdoba. Facultad de Ciencias Químicas. Instituto de Investigaciones en Físico-química de Córdoba; Argentina
dc.description.fil
Fil: Allende, Leandro German. Consejo Nacional de Investigaciones Científicas y Técnicas. Centro Científico Tecnológico Conicet - Córdoba. Instituto de Investigaciones en Físico-química de Córdoba. Universidad Nacional de Córdoba. Facultad de Ciencias Químicas. Instituto de Investigaciones en Físico-química de Córdoba; Argentina
dc.description.fil
Fil: Veglia, Alicia Viviana. Consejo Nacional de Investigaciones Científicas y Técnicas. Centro Científico Tecnológico Conicet - Córdoba. Instituto de Investigaciones en Físico-química de Córdoba. Universidad Nacional de Córdoba. Facultad de Ciencias Químicas. Instituto de Investigaciones en Físico-química de Córdoba; Argentina
dc.description.fil
Fil: Coronado, Eduardo A.. Consejo Nacional de Investigaciones Científicas y Técnicas. Centro Científico Tecnológico Conicet - Córdoba. Instituto de Investigaciones en Físico-química de Córdoba. Universidad Nacional de Córdoba. Facultad de Ciencias Químicas. Instituto de Investigaciones en Físico-química de Córdoba; Argentina
dc.journal.title
Journal of Physical Chemistry C

dc.relation.alternativeid
info:eu-repo/semantics/altIdentifier/url/http://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/acs.jpcc.5b01647
dc.relation.alternativeid
info:eu-repo/semantics/altIdentifier/doi/http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpcc.5b01647
Archivos asociados