Mostrar el registro sencillo del ítem
dc.contributor.author
Bueren Calabuig, Juan A.
dc.contributor.author
Pierdominici Sottile, Gustavo

dc.contributor.author
Roitberg, Adrián

dc.date.available
2018-01-17T21:46:58Z
dc.date.issued
2014-05
dc.identifier.citation
Bueren Calabuig, Juan A.; Pierdominici Sottile, Gustavo; Roitberg, Adrián; Unraveling the Differences of the Hydrolytic Activity of Trypanosoma cruzi trans-Sialidase and Trypanosoma rangeli Sialidase: A Quantum Mechanics–Molecular Mechanics Modeling Study; American Chemical Society; Journal of Physical Chemistry B; 118; 22; 5-2014; 5807-5816
dc.identifier.issn
1520-6106
dc.identifier.uri
http://hdl.handle.net/11336/33742
dc.description.abstract
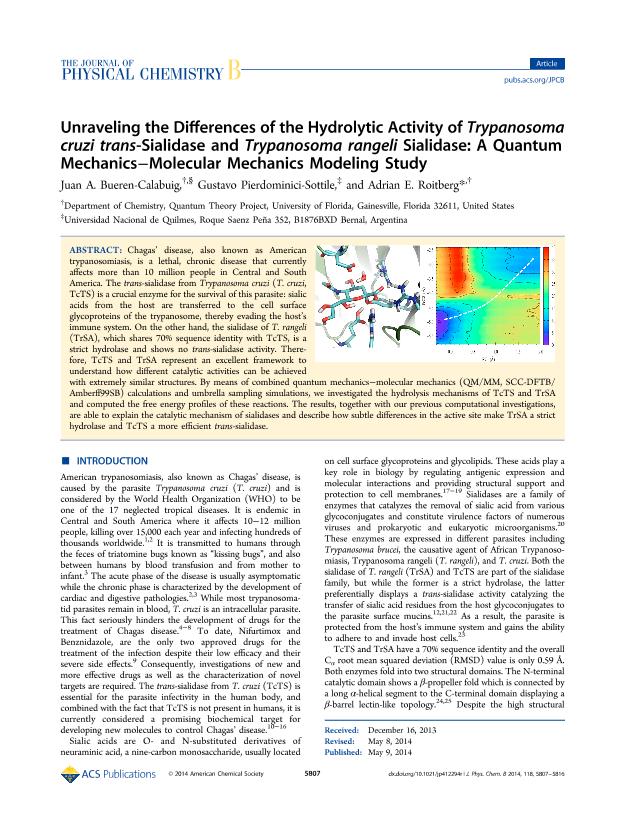
Chagas’ disease, also known as American trypanosomiasis, is a lethal, chronic disease that currently affects more than 10 million people in Central and South America. The trans-sialidase from Trypanosoma cruzi (T. cruzi, TcTS) is a crucial enzyme for the survival of this parasite: sialic acids from the host are transferred to the cell surface glycoproteins of the trypanosome, thereby evading the host’s immune system. On the other hand, the sialidase of T. rangeli (TrSA), which shares 70% sequence identity with TcTS, is a strict hydrolase and shows no trans-sialidase activity. Therefore, TcTS and TrSA represent an excellent framework to understand how different catalytic activities can be achieved with extremely similar structures. By means of combined quantum mechanics–molecular mechanics (QM/MM, SCC-DFTB/Amberff99SB) calculations and umbrella sampling simulations, we investigated the hydrolysis mechanisms of TcTS and TrSA and computed the free energy profiles of these reactions. The results, together with our previous computational investigations, are able to explain the catalytic mechanism of sialidases and describe how subtle differences in the active site make TrSA a strict hydrolase and TcTS a more efficient trans-sialidase.
dc.format
application/pdf
dc.language.iso
eng
dc.publisher
American Chemical Society

dc.rights
info:eu-repo/semantics/openAccess
dc.rights.uri
https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/2.5/ar/
dc.subject
Qmmm
dc.subject
Umbrella
dc.subject
Catalysis
dc.subject
Sialidase
dc.subject.classification
Otras Ciencias Químicas

dc.subject.classification
Ciencias Químicas

dc.subject.classification
CIENCIAS NATURALES Y EXACTAS

dc.title
Unraveling the Differences of the Hydrolytic Activity of Trypanosoma cruzi trans-Sialidase and Trypanosoma rangeli Sialidase: A Quantum Mechanics–Molecular Mechanics Modeling Study
dc.type
info:eu-repo/semantics/article
dc.type
info:ar-repo/semantics/artículo
dc.type
info:eu-repo/semantics/publishedVersion
dc.date.updated
2018-01-16T18:03:28Z
dc.journal.volume
118
dc.journal.number
22
dc.journal.pagination
5807-5816
dc.journal.pais
Estados Unidos

dc.journal.ciudad
Washington, DC
dc.description.fil
Fil: Bueren Calabuig, Juan A.. University of Florida; Estados Unidos
dc.description.fil
Fil: Pierdominici Sottile, Gustavo. Universidad Nacional de Quilmes; Argentina. Consejo Nacional de Investigaciones Científicas y Técnicas; Argentina
dc.description.fil
Fil: Roitberg, Adrián. University of Florida; Estados Unidos
dc.journal.title
Journal of Physical Chemistry B

dc.relation.alternativeid
info:eu-repo/semantics/altIdentifier/url/http://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/jp412294r
dc.relation.alternativeid
info:eu-repo/semantics/altIdentifier/doi/http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1021/jp412294r
dc.relation.alternativeid
info:eu-repo/semantics/altIdentifier/url/https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4051249/
Archivos asociados