Artículo
A Theoretical Study of the Effect of Zr-, Nb-Doped and Vacancy-like Defects on H Desorption on MgH2 (110) Surface
Fecha de publicación:
02/2014
Editorial:
American Chemical Society
Revista:
Journal of Physical Chemistry C
ISSN:
1932-7447
Idioma:
Inglés
Tipo de recurso:
Artículo publicado
Clasificación temática:
Resumen
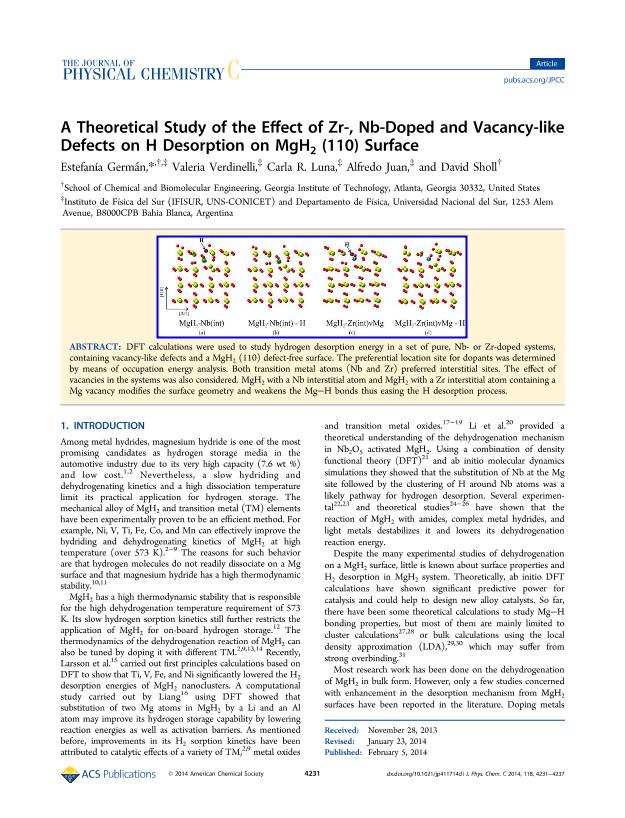
DFT calculations were used to study hydrogen desorption energy in a set of pure, Nb- or Zr-doped systems, containing vacancy-like defects and a MgH2 (110) defect-free surface. The preferential location site for dopants was determined by means of occupation energy analysis. Both transition metal atoms (Nb and Zr) preferred interstitial sites. The effect of vacancies in the systems was also considered. MgH2 with a Nb interstitial atom and MgH2 with a Zr interstitial atom containing a Mg vacancy modifies the surface geometry and weakens the Mg–H bonds thus easing the H desorption process.
Palabras clave:
Mgh2
,
Zr-Doped
,
Nb-Doped
,
H Desorption
Archivos asociados
Licencia
Identificadores
Colecciones
Articulos(IFISUR)
Articulos de INSTITUTO DE FISICA DEL SUR
Articulos de INSTITUTO DE FISICA DEL SUR
Citación
German, Estefania; Verdinelli, Valeria; Luna, Carla Romina; Juan, Alfredo; Sholl, David ; A Theoretical Study of the Effect of Zr-, Nb-Doped and Vacancy-like Defects on H Desorption on MgH2 (110) Surface; American Chemical Society; Journal of Physical Chemistry C; 118; 8; 2-2014; 4231-4237
Compartir
Altmétricas