Mostrar el registro sencillo del ítem
dc.contributor.author
Rodriguez Aguilar, Leandro Pedro Faustino

dc.contributor.author
Cedeño Viteri, Marco Vinicio

dc.contributor.author
Sanchez, Mabel Cristina

dc.date.available
2017-10-23T18:49:48Z
dc.date.issued
2016-07-25
dc.identifier.citation
Rodriguez Aguilar, Leandro Pedro Faustino; Cedeño Viteri, Marco Vinicio; Sanchez, Mabel Cristina; Sensor location for enhancing fault diagnosis; American Chemical Society; Industrial & Engineering Chemical Research; 55; 32; 25-7-2016; 8830-8836
dc.identifier.issn
0888-5885
dc.identifier.uri
http://hdl.handle.net/11336/26925
dc.description.abstract
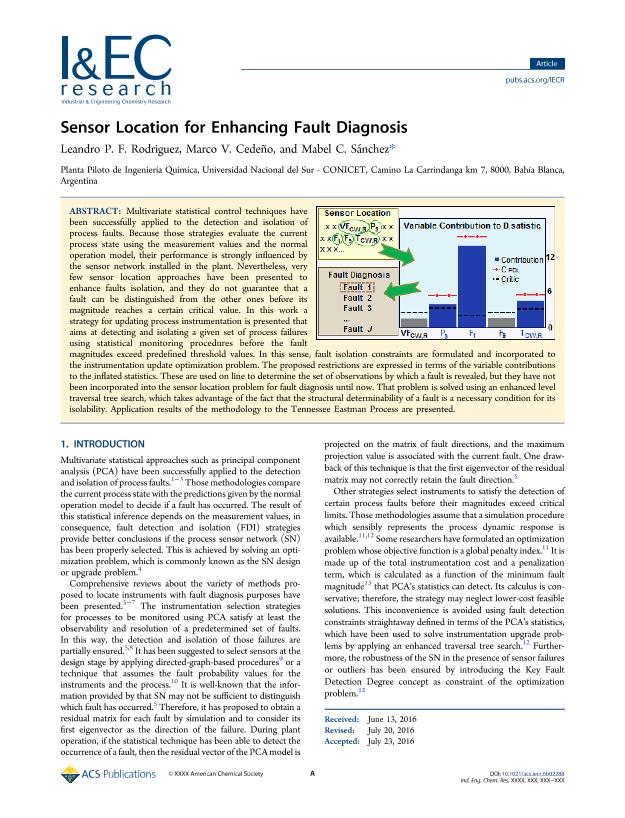
Multivariate statistical control techniques have been successfully applied to the detection and isolation of process faults. Because those strategies evaluate the current process state using the measurement values and the normal operation model, their performance is strongly influenced by the sensor network installed in the plant. Nevertheless very few sensor location approaches have been presented to enhance faults isolation, and they do not guarantee that a fault can be distinguished from the other ones before its magnitude reaches a certain critical value. In this work a strategy for updating process instrumentation is presented that aims at detecting and isolating a given set of process failures using statistical monitoring procedures before the fault magnitudes exceed predefined threshold values. In this sense fault isolation constraints are formulated and incorporated to the instrumentation update optimization problem. The proposed restrictions are expressed in terms of the variable contributions to the inflated statistics. These are used on line to determine the set of observations by which a fault is revealed, but they have not been incorporated into the sensor location problem for fault diagnosis until now. That problem is solved using an enhanced level traversal tree search, which takes advantage of the fact that the structural determinability of a fault is a necessary condition for its isolability. Application results of the methodology to the Tennessee Eastman Process are presented.
dc.format
application/pdf
dc.language.iso
eng
dc.publisher
American Chemical Society

dc.rights
info:eu-repo/semantics/openAccess
dc.rights.uri
https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/2.5/ar/
dc.subject
Sensor Network Design
dc.subject
Principal Component Analysis
dc.subject.classification
Otras Ingeniería Química

dc.subject.classification
Ingeniería Química

dc.subject.classification
INGENIERÍAS Y TECNOLOGÍAS

dc.title
Sensor location for enhancing fault diagnosis
dc.type
info:eu-repo/semantics/article
dc.type
info:ar-repo/semantics/artículo
dc.type
info:eu-repo/semantics/publishedVersion
dc.date.updated
2017-10-09T15:33:52Z
dc.journal.volume
55
dc.journal.number
32
dc.journal.pagination
8830-8836
dc.journal.pais
Estados Unidos

dc.journal.ciudad
Washington D. C.
dc.description.fil
Fil: Rodriguez Aguilar, Leandro Pedro Faustino. Consejo Nacional de Investigaciones Científicas y Técnicas. Centro Científico Tecnológico Conicet - Bahía Blanca. Planta Piloto de Ingeniería Química. Universidad Nacional del Sur. Planta Piloto de Ingeniería Química; Argentina
dc.description.fil
Fil: Cedeño Viteri, Marco Vinicio. Consejo Nacional de Investigaciones Científicas y Técnicas. Centro Científico Tecnológico Conicet - Bahía Blanca. Planta Piloto de Ingeniería Química. Universidad Nacional del Sur. Planta Piloto de Ingeniería Química; Argentina
dc.description.fil
Fil: Sanchez, Mabel Cristina. Consejo Nacional de Investigaciones Científicas y Técnicas. Centro Científico Tecnológico Conicet - Bahía Blanca. Planta Piloto de Ingeniería Química. Universidad Nacional del Sur. Planta Piloto de Ingeniería Química; Argentina
dc.journal.title
Industrial & Engineering Chemical Research

dc.relation.alternativeid
info:eu-repo/semantics/altIdentifier/doi/http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/acs.iecr.6b02288
dc.relation.alternativeid
info:eu-repo/semantics/altIdentifier/url/http://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/acs.iecr.6b02288
Archivos asociados