Mostrar el registro sencillo del ítem
dc.contributor.author
Durantini, Andres Matías

dc.contributor.author
Falcone, Ruben Dario

dc.contributor.author
Chessa, Juana Josefa

dc.contributor.author
Correa, Nestor Mariano

dc.date.available
2017-08-24T20:30:02Z
dc.date.issued
2013-03
dc.identifier.citation
Durantini, Andres Matías; Falcone, Ruben Dario; Chessa, Juana Josefa; Correa, Nestor Mariano; More evidence on the control of reverse micelles sizes: combination of different techniques as a powerful tool to monitor AOT reversed micelles properties; American Chemical Society; Journal of Physical Chemistry B; 117; 14; 3-2013; 3818-3828
dc.identifier.issn
1089-5647
dc.identifier.uri
http://hdl.handle.net/11336/22972
dc.description.abstract
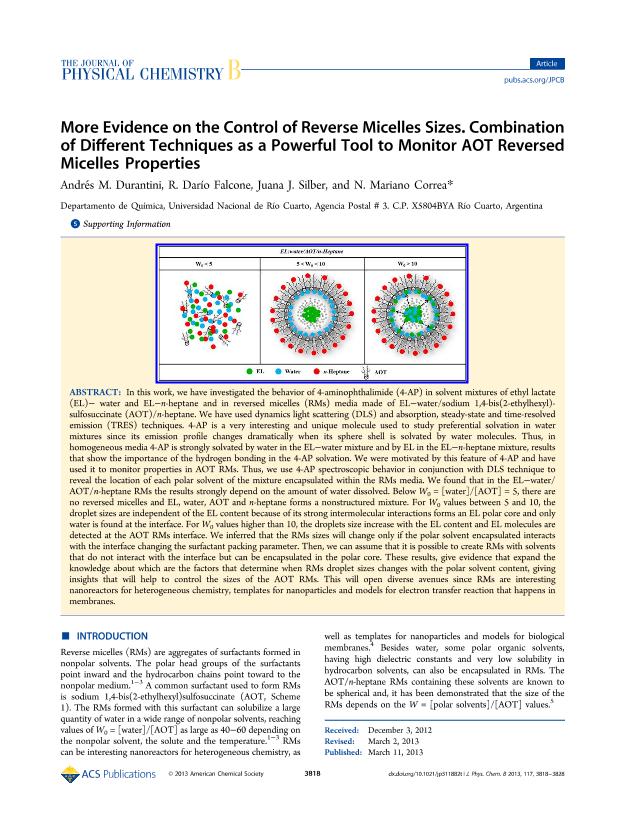
In this work, we have investigated the behavior of 4-aminophthalimide (4-AP) in solvent mixtures of ethyl lactate (EL)− water and EL−n-heptane and in reversed micelles (RMs) media made of EL−water/sodium 1,4-bis(2-ethylhexyl)- sulfosuccinate (AOT)/n-heptane. We have used dynamics light scattering (DLS) and absorption, steady-state and time-resolved emission (TRES) techniques. 4-AP is a very interesting and unique molecule used to study preferential solvation in water mixtures since its emission profile changes dramatically when its sphere shell is solvated by water molecules. Thus, in homogeneous media 4-AP is strongly solvated by water in the EL−water mixture and by EL in the EL−n-heptane mixture, results that show the importance of the hydrogen bonding in the 4-AP solvation. We were motivated by this feature of 4-AP and have used it to monitor properties in AOT RMs. Thus, we use 4-AP spectroscopic behavior in conjunction with DLS technique to reveal the location of each polar solvent of the mixture encapsulated within the RMs media. We found that in the EL−water/ AOT/n-heptane RMs the results strongly depend on the amount of water dissolved. Below W0 = [water]/[AOT] = 5, there are no reversed micelles and EL, water, AOT and n-heptane forms a nonstructured mixture. For W0 values between 5 and 10, the droplet sizes are independent of the EL content because of its strong intermolecular interactions forms an EL polar core and only water is found at the interface. For W0 values higher than 10, the droplets size increase with the EL content and EL molecules are detected at the AOT RMs interface. We inferred that the RMs sizes will change only if the polar solvent encapsulated interacts with the interface changing the surfactant packing parameter. Then, we can assume that it is possible to create RMs with solvents that do not interact with the interface but can be encapsulated in the polar core. These results, give evidence that expand the knowledge about which are the factors that determine when RMs droplet sizes changes with the polar solvent content, giving insights that will help to control the sizes of the AOT RMs. This will open diverse avenues since RMs are interesting nanoreactors for heterogeneous chemistry, templates for nanoparticles and models for electron transfer reaction that happens in membranes.
dc.format
application/pdf
dc.language.iso
eng
dc.publisher
American Chemical Society

dc.rights
info:eu-repo/semantics/openAccess
dc.rights.uri
https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/2.5/ar/
dc.subject
4-Aminophthalimide
dc.subject
Ethyl Lactate
dc.subject
Reverse Micelles
dc.subject
Time-Resolved
dc.subject.classification
Otras Ciencias Químicas

dc.subject.classification
Ciencias Químicas

dc.subject.classification
CIENCIAS NATURALES Y EXACTAS

dc.title
More evidence on the control of reverse micelles sizes: combination of different techniques as a powerful tool to monitor AOT reversed micelles properties
dc.type
info:eu-repo/semantics/article
dc.type
info:ar-repo/semantics/artículo
dc.type
info:eu-repo/semantics/publishedVersion
dc.date.updated
2017-08-24T18:02:58Z
dc.journal.volume
117
dc.journal.number
14
dc.journal.pagination
3818-3828
dc.journal.pais
Estados Unidos

dc.journal.ciudad
Washington DC
dc.description.fil
Fil: Durantini, Andres Matías. Universidad Nacional de Río Cuarto. Facultad de Ciencias Exactas Fisicoquímicas y Naturales. Departamento de Química; Argentina. Consejo Nacional de Investigaciones Científicas y Técnicas; Argentina
dc.description.fil
Fil: Falcone, Ruben Dario. Universidad Nacional de Río Cuarto. Facultad de Ciencias Exactas Fisicoquímicas y Naturales. Departamento de Química; Argentina. Consejo Nacional de Investigaciones Científicas y Técnicas; Argentina
dc.description.fil
Fil: Chessa, Juana Josefa. Universidad Nacional de Río Cuarto. Facultad de Ciencias Exactas Fisicoquímicas y Naturales. Departamento de Química; Argentina. Consejo Nacional de Investigaciones Científicas y Técnicas; Argentina
dc.description.fil
Fil: Correa, Nestor Mariano. Universidad Nacional de Río Cuarto. Facultad de Ciencias Exactas Fisicoquímicas y Naturales. Departamento de Química; Argentina. Consejo Nacional de Investigaciones Científicas y Técnicas; Argentina
dc.journal.title
Journal of Physical Chemistry B

dc.relation.alternativeid
info:eu-repo/semantics/altIdentifier/doi/http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/jp311882t
dc.relation.alternativeid
info:eu-repo/semantics/altIdentifier/url/http://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/jp311882t
Archivos asociados