Mostrar el registro sencillo del ítem
dc.contributor.author
Onnainty, Renée

dc.contributor.author
Schenfeld, Esteban Martin

dc.contributor.author
Quevedo, Mario Alfredo

dc.contributor.author
Fernández, Mariana Adela

dc.contributor.author
Longhi, Marcela Raquel

dc.contributor.author
Granero, Gladys Ester

dc.date.available
2017-08-23T17:14:40Z
dc.date.issued
2012-12
dc.identifier.citation
Onnainty, Renée; Schenfeld, Esteban Martin; Quevedo, Mario Alfredo; Fernández, Mariana Adela; Longhi, Marcela Raquel; et al.; Characterization of the Hydrochlorothiazide: β-Cyclodextrin Inclusion Complex. Experimental and Theoretical Methods; American Chemical Society; Journal of Physical Chemistry B; 117; 1; 12-2012; 206-217
dc.identifier.issn
1520-6106
dc.identifier.uri
http://hdl.handle.net/11336/22838
dc.description.abstract
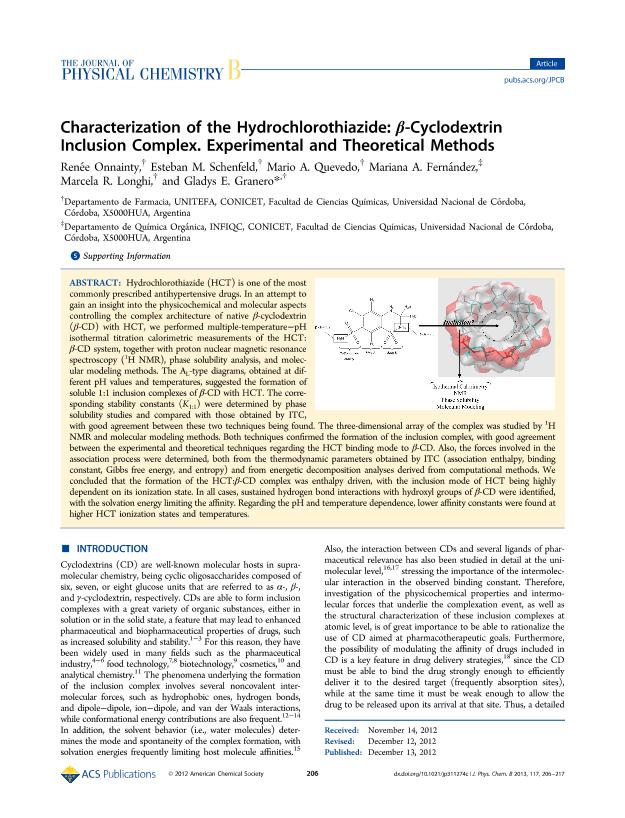
Hydrochlorothiazide (HCT) is one of the most commonly prescribed antihypertensive drugs. In an attempt to gain an insight into the physicochemical and molecular aspects controlling the complex architecture of native β-cyclodextrin (β-CD) with HCT, we performed multiple-temperature−pH isothermal titration calorimetric measurements of the HCT: β-CD system, together with proton nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy (1 H NMR), phase solubility analysis, and molecular modeling methods. The AL-type diagrams, obtained at different pH values and temperatures, suggested the formation of soluble 1:1 inclusion complexes of β-CD with HCT. The corresponding stability constants (K1:1) were determined by phase solubility studies and compared with those obtained by ITC, with good agreement between these two techniques being found. The three-dimensional array of the complex was studied by 1 H NMR and molecular modeling methods. Both techniques confirmed the formation of the inclusion complex, with good agreement between the experimental and theoretical techniques regarding the HCT binding mode to β-CD. Also, the forces involved in the association process were determined, both from the thermodynamic parameters obtained by ITC (association enthalpy, binding constant, Gibbs free energy, and entropy) and from energetic decomposition analyses derived from computational methods. We concluded that the formation of the HCT:β-CD complex was enthalpy driven, with the inclusion mode of HCT being highly dependent on its ionization state. In all cases, sustained hydrogen bond interactions with hydroxyl groups of β-CD were identified, with the solvation energy limiting the affinity. Regarding the pH and temperature dependence, lower affinity constants were found at higher HCT ionization states and temperatures.
dc.format
application/pdf
dc.language.iso
eng
dc.publisher
American Chemical Society

dc.rights
info:eu-repo/semantics/openAccess
dc.rights.uri
https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/2.5/ar/
dc.subject
Hydrochlortiazida
dc.subject
Cyclodextrin
dc.subject
Complexes
dc.subject.classification
Otras Ciencias Químicas

dc.subject.classification
Ciencias Químicas

dc.subject.classification
CIENCIAS NATURALES Y EXACTAS

dc.title
Characterization of the Hydrochlorothiazide: β-Cyclodextrin Inclusion Complex. Experimental and Theoretical Methods
dc.type
info:eu-repo/semantics/article
dc.type
info:ar-repo/semantics/artículo
dc.type
info:eu-repo/semantics/publishedVersion
dc.date.updated
2017-08-18T14:59:49Z
dc.journal.volume
117
dc.journal.number
1
dc.journal.pagination
206-217
dc.journal.pais
Estados Unidos

dc.journal.ciudad
Washington DC
dc.description.fil
Fil: Onnainty, Renée. Consejo Nacional de Investigaciones Científicas y Técnicas. Centro Científico Tecnológico Conicet - Córdoba. Unidad de Investigación y Desarrollo en Tecnología Farmacéutica. Universidad Nacional de Córdoba. Facultad de Ciencias Químicas. Unidad de Investigación y Desarrollo en Tecnología Farmacéutica; Argentina
dc.description.fil
Fil: Schenfeld, Esteban Martin. Consejo Nacional de Investigaciones Científicas y Técnicas. Centro Científico Tecnológico Conicet - Córdoba. Unidad de Investigación y Desarrollo en Tecnología Farmacéutica. Universidad Nacional de Córdoba. Facultad de Ciencias Químicas. Unidad de Investigación y Desarrollo en Tecnología Farmacéutica; Argentina
dc.description.fil
Fil: Quevedo, Mario Alfredo. Consejo Nacional de Investigaciones Científicas y Técnicas. Centro Científico Tecnológico Conicet - Córdoba. Unidad de Investigación y Desarrollo en Tecnología Farmacéutica. Universidad Nacional de Córdoba. Facultad de Ciencias Químicas. Unidad de Investigación y Desarrollo en Tecnología Farmacéutica; Argentina
dc.description.fil
Fil: Fernández, Mariana Adela. Consejo Nacional de Investigaciones Científicas y Técnicas. Centro Científico Tecnológico Conicet - Córdoba. Instituto de Investigaciones en Físico-química de Córdoba. Universidad Nacional de Córdoba. Facultad de Ciencias Químicas. Instituto de Investigaciones en Físico-química de Córdoba; Argentina
dc.description.fil
Fil: Longhi, Marcela Raquel. Consejo Nacional de Investigaciones Científicas y Técnicas. Centro Científico Tecnológico Conicet - Córdoba. Unidad de Investigación y Desarrollo en Tecnología Farmacéutica. Universidad Nacional de Córdoba. Facultad de Ciencias Químicas. Unidad de Investigación y Desarrollo en Tecnología Farmacéutica; Argentina
dc.description.fil
Fil: Granero, Gladys Ester. Consejo Nacional de Investigaciones Científicas y Técnicas. Centro Científico Tecnológico Conicet - Córdoba. Unidad de Investigación y Desarrollo en Tecnología Farmacéutica. Universidad Nacional de Córdoba. Facultad de Ciencias Químicas. Unidad de Investigación y Desarrollo en Tecnología Farmacéutica; Argentina
dc.journal.title
Journal of Physical Chemistry B

dc.relation.alternativeid
info:eu-repo/semantics/altIdentifier/doi/http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/jp311274c
dc.relation.alternativeid
info:eu-repo/semantics/altIdentifier/url/http://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/jp311274c
Archivos asociados