Artículo
Acute and chronic physical activity improves spatial memory in an immersive virtual reality task
Ramírez Butavand, Daniela ; Rodríguez, María Florencia
; Rodríguez, María Florencia ; Cifuentes, Maria Virginia
; Cifuentes, Maria Virginia ; Miranda, Magdalena
; Miranda, Magdalena ; Garcia Bauza, Cristian Dario
; Garcia Bauza, Cristian Dario ; Bekinschtein, Pedro Alejandro
; Bekinschtein, Pedro Alejandro ; Ballarini, Fabricio Matias
; Ballarini, Fabricio Matias
 ; Rodríguez, María Florencia
; Rodríguez, María Florencia ; Cifuentes, Maria Virginia
; Cifuentes, Maria Virginia ; Miranda, Magdalena
; Miranda, Magdalena ; Garcia Bauza, Cristian Dario
; Garcia Bauza, Cristian Dario ; Bekinschtein, Pedro Alejandro
; Bekinschtein, Pedro Alejandro ; Ballarini, Fabricio Matias
; Ballarini, Fabricio Matias
Fecha de publicación:
03/2023
Editorial:
Elsevier
Revista:
iScience
ISSN:
2589-0042
Idioma:
Inglés
Tipo de recurso:
Artículo publicado
Clasificación temática:
Resumen
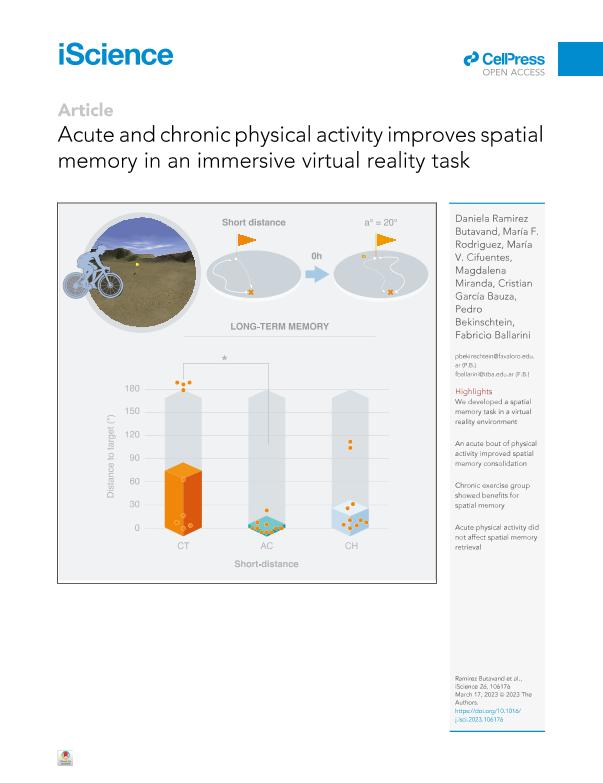
Physical activity benefits both fitness and cognition. However, its effect on long-term memory is unclear. In this study, we evaluated the effect of acute and chronic exercise on long-term spatial memory for a new virtual reality task. Participants were immersed in the virtual environment and navigated a wide arena that included target objects. We assessed spatial memory in two conditions (encoded targets separated by a short or long distance) and found that 25 min of cycling after encoding — but not before retrieval — was sufficient to improve the long-term memory retention for the short, but not for the long distance. Furthermore, we found that participants who engaged in regular physical activity showed memory for the short-distance condition whereas controls did not. Thus, physical activity could be a simple way to improve spatial memories.
Archivos asociados
Licencia
Identificadores
Colecciones
Articulos(CCT - TANDIL)
Articulos de CTRO CIENTIFICO TECNOLOGICO CONICET - TANDIL
Articulos de CTRO CIENTIFICO TECNOLOGICO CONICET - TANDIL
Articulos(INCYT)
Articulos de INSTITUTO DE NEUROCIENCIAS COGNITIVAS Y TRASLACIONAL
Articulos de INSTITUTO DE NEUROCIENCIAS COGNITIVAS Y TRASLACIONAL
Citación
Ramírez Butavand, Daniela; Rodríguez, María Florencia; Cifuentes, Maria Virginia; Miranda, Magdalena; Garcia Bauza, Cristian Dario; et al.; Acute and chronic physical activity improves spatial memory in an immersive virtual reality task; Elsevier; iScience; 26; 3; 3-2023; 1-14
Compartir
Altmétricas