Artículo
Decrease of ERK/MAPK overactivation in prefrontal cortex reverses early memory deficit in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease
Feld, Mariana ; Krawczyk, Maria del Carmen
; Krawczyk, Maria del Carmen ; Fustiñana, María Sol
; Fustiñana, María Sol ; Blake, Mariano Guillermo
; Blake, Mariano Guillermo ; Baratti, Carlos Maria
; Baratti, Carlos Maria ; Romano, Arturo Gabriel
; Romano, Arturo Gabriel ; Boccia, Mariano Martin
; Boccia, Mariano Martin
 ; Krawczyk, Maria del Carmen
; Krawczyk, Maria del Carmen ; Fustiñana, María Sol
; Fustiñana, María Sol ; Blake, Mariano Guillermo
; Blake, Mariano Guillermo ; Baratti, Carlos Maria
; Baratti, Carlos Maria ; Romano, Arturo Gabriel
; Romano, Arturo Gabriel ; Boccia, Mariano Martin
; Boccia, Mariano Martin
Fecha de publicación:
11/2013
Editorial:
Ios Press
Revista:
Journal Of Alzheimer's Disease
ISSN:
1387-2877
e-ISSN:
1875-8908
Idioma:
Inglés
Tipo de recurso:
Artículo publicado
Clasificación temática:
Resumen
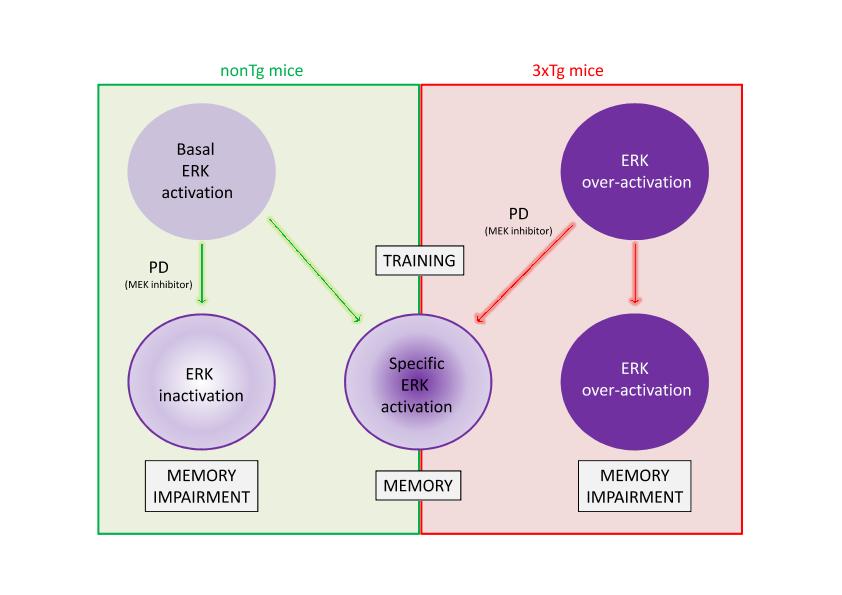
Alzheimer's disease (AD) can be considered as a disease of memory in its initial clinical stages. Amyloid-β (Aβ) peptide accumulation is central to the disease initiation leading later to intracellular neurofibrillary tangles (NFTs) of cytoskeletal tau protein formation. It is under discussion whether different Aβ levels of aggregation, concentration, brain area, and/or time of exposure might be critical to the disease progression, as well as which intracellular pathways it activates. The aim of the present work was to study memory-related early molecular and behavioral alterations in a mouse model of AD, in which a subtle deregulation of the physiologic function of Aβ can be inferred. For this purpose we used triple-transgenic (3xTg) mice, which develop Aβ and tau pathology resembling the disease progression in humans. Memory impairment in novel object recognition task was evident by 5 months of age in 3xTg mice. Hippocampus and prefrontal cortex extra-nuclear protein extracts developed differential patterns of Aβ aggregation. ERK1/MAPK showed higher levels of cytosolic activity at 3 months and higher levels of nuclear activity at 6 months in the prefrontal cortex. No significant differences were found in JNK and NF-κB activity and in calcineurin protein levels. Finally, intra-PFC administration of a MEK inhibitor in 6-month-old 3xTg mice was able to reverse memory impairment, suggesting that ERK pathway alterations might at least partially explain memory deficits observed in this model, likely as a consequence of memory trace disruption.
Archivos asociados
Licencia
Identificadores
Colecciones
Articulos(IFIBYNE)
Articulos de INST.DE FISIOL., BIOL.MOLECULAR Y NEUROCIENCIAS
Articulos de INST.DE FISIOL., BIOL.MOLECULAR Y NEUROCIENCIAS
Articulos(OCA HOUSSAY)
Articulos de OFICINA DE COORDINACION ADMINISTRATIVA HOUSSAY
Articulos de OFICINA DE COORDINACION ADMINISTRATIVA HOUSSAY
Citación
Feld, Mariana; Krawczyk, Maria del Carmen; Fustiñana, María Sol; Blake, Mariano Guillermo; Baratti, Carlos Maria; et al.; Decrease of ERK/MAPK overactivation in prefrontal cortex reverses early memory deficit in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease; Ios Press; Journal Of Alzheimer's Disease; 40; 1; 11-2013; 69-82
Compartir
Altmétricas