Artículo
Confinement Effects in Protonation Reactions Catalyzed by Zeolites with Large Void Structures
Zalazar, Maria Fernanda ; Cabral, Néstor Damián; Romero Ojeda, Gonzalo D.; Alegre, Clara Iris Aymará
; Cabral, Néstor Damián; Romero Ojeda, Gonzalo D.; Alegre, Clara Iris Aymará ; Peruchena, Nelida Maria
; Peruchena, Nelida Maria
 ; Cabral, Néstor Damián; Romero Ojeda, Gonzalo D.; Alegre, Clara Iris Aymará
; Cabral, Néstor Damián; Romero Ojeda, Gonzalo D.; Alegre, Clara Iris Aymará ; Peruchena, Nelida Maria
; Peruchena, Nelida Maria
Fecha de publicación:
12/2018
Editorial:
American Chemical Society
Revista:
Journal of Physical Chemistry C
ISSN:
1932-7447
Idioma:
Inglés
Tipo de recurso:
Artículo publicado
Clasificación temática:
Resumen
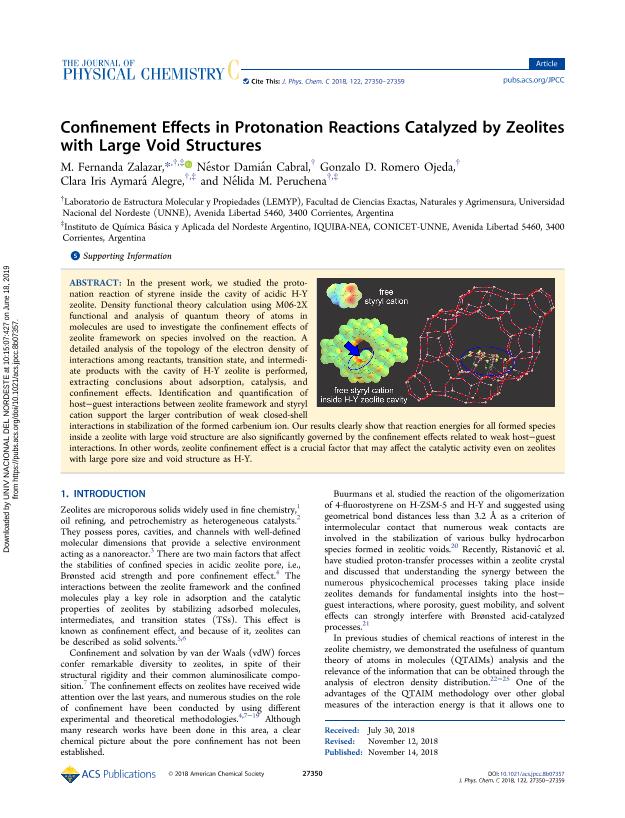
In the present work, we studied the protonation reaction of styrene inside the cavity of acidic H-Y zeolite. Density functional theory calculation using M06-2X functional and analysis of quantum theory of atoms in molecules are used to investigate the confinement effects of zeolite framework on species involved on the reaction. A detailed analysis of the topology of the electron density of interactions among reactants, transition state, and intermediate products with the cavity of H-Y zeolite is performed, extracting conclusions about adsorption, catalysis, and confinement effects. Identification and quantification of host-guest interactions between zeolite framework and styryl cation support the larger contribution of weak closed-shell interactions in stabilization of the formed carbenium ion. Our results clearly show that reaction energies for all formed species inside a zeolite with large void structure are also significantly governed by the confinement effects related to weak host-guest interactions. In other words, zeolite confinement effect is a crucial factor that may affect the catalytic activity even on zeolites with large pore size and void structure as H-Y.
Palabras clave:
Zeolites
,
Confinement Effects
,
heterogeneous catalysts
,
QTAIM
Archivos asociados
Licencia
Identificadores
Colecciones
Articulos(CCT - NORDESTE)
Articulos de CTRO.CIENTIFICO TECNOL.CONICET - NORDESTE
Articulos de CTRO.CIENTIFICO TECNOL.CONICET - NORDESTE
Articulos(IQUIBA-NEA)
Articulos de INSTITUTO DE QUIMICA BASICA Y APLICADA DEL NORDESTE ARGENTINO
Articulos de INSTITUTO DE QUIMICA BASICA Y APLICADA DEL NORDESTE ARGENTINO
Citación
Zalazar, Maria Fernanda; Cabral, Néstor Damián; Romero Ojeda, Gonzalo D.; Alegre, Clara Iris Aymará; Peruchena, Nelida Maria; Confinement Effects in Protonation Reactions Catalyzed by Zeolites with Large Void Structures; American Chemical Society; Journal of Physical Chemistry C; 122; 48; 12-2018; 27350-27359
Compartir
Altmétricas