Mostrar el registro sencillo del ítem
dc.contributor.author
Balashankar, Vishal Subramanian
dc.contributor.author
Rajagopalan, Ashwin Kumar

dc.contributor.author
De Pauw, R.
dc.contributor.author
Avila, Adolfo María

dc.contributor.author
Rajendran, Arvind

dc.date.available
2020-11-26T13:55:04Z
dc.date.issued
2019-02
dc.identifier.citation
Balashankar, Vishal Subramanian; Rajagopalan, Ashwin Kumar; De Pauw, R.; Avila, Adolfo María; Rajendran, Arvind; Analysis of a Batch Adsorber Analogue for Rapid Screening of Adsorbents for Postcombustion CO 2 Capture; American Chemical Society; Industrial & Engineering Chemical Research; 58; 8; 2-2019; 3314-3328
dc.identifier.issn
0888-5885
dc.identifier.uri
http://hdl.handle.net/11336/119059
dc.description.abstract
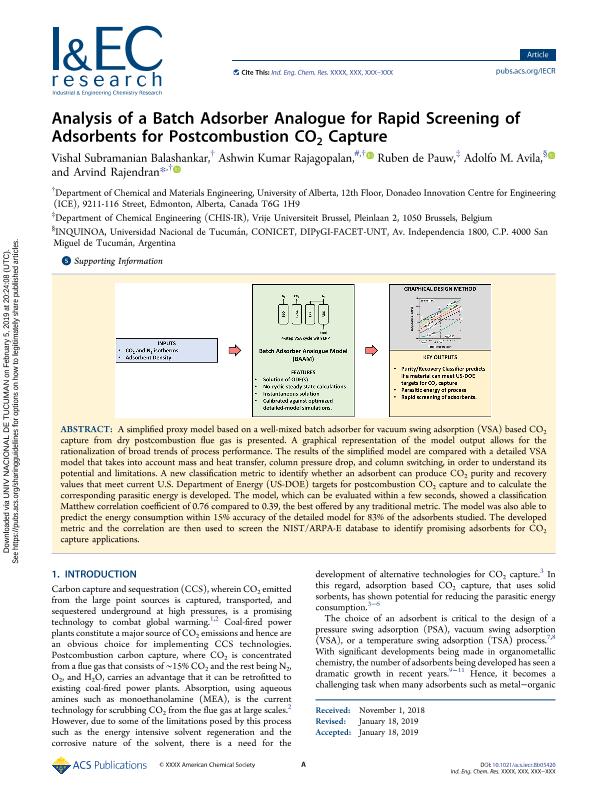
A simplified proxy model based on a well-mixed batch adsorber for vacuum swing adsorption (VSA) based CO2 capture from dry post-combustion flue gas is presented. A graphical representation of the model output allows for the rationalization of broad trends of process performance. The results of the simplified model are compared with a detailed VSA model that takes into account mass and heat transfer, column pressure drop and column switching, in order to understand its potential and limitations. A new classification metric to identify whether an adsorbent can produce CO2 purity and recovery that meet current US Department of Energy (US-DOE) for post-combustion CO2 capture and to calculate the corresponding parasitic energy is developed. The model, which can be evaluated within a few seconds, showed a classification Matthew correlation coefficient of 0.76 compared to 0.39, the best offered by any traditional metric. The model was also able to predict the energy consumption within 15% accuracy of the detailed model for 83% of the adsorbents studied. The developed metric and the correlation are then used to screen NIST/ARPA-E database to identify promising adsorbents for CO2 capture applications.
dc.format
application/pdf
dc.language.iso
eng
dc.publisher
American Chemical Society

dc.rights
info:eu-repo/semantics/openAccess
dc.rights.uri
https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/2.5/ar/
dc.subject
Adsorption
dc.subject
CO2 capture
dc.subject
Adsobent screening
dc.subject
PSA
dc.subject.classification
Ingeniería de Procesos Químicos

dc.subject.classification
Ingeniería Química

dc.subject.classification
INGENIERÍAS Y TECNOLOGÍAS

dc.title
Analysis of a Batch Adsorber Analogue for Rapid Screening of Adsorbents for Postcombustion CO 2 Capture
dc.type
info:eu-repo/semantics/article
dc.type
info:ar-repo/semantics/artículo
dc.type
info:eu-repo/semantics/publishedVersion
dc.date.updated
2020-11-17T18:39:07Z
dc.journal.volume
58
dc.journal.number
8
dc.journal.pagination
3314-3328
dc.journal.pais
Estados Unidos

dc.description.fil
Fil: Balashankar, Vishal Subramanian. University of Alberta; Canadá
dc.description.fil
Fil: Rajagopalan, Ashwin Kumar. University of Alberta; Canadá
dc.description.fil
Fil: De Pauw, R.. Vrije Unviversiteit Brussel; Bélgica
dc.description.fil
Fil: Avila, Adolfo María. Consejo Nacional de Investigaciones Científicas y Técnicas. Centro Científico Tecnológico Conicet - Tucumán. Instituto de Química del Noroeste. Universidad Nacional de Tucumán. Facultad de Bioquímica, Química y Farmacia. Instituto de Química del Noroeste; Argentina
dc.description.fil
Fil: Rajendran, Arvind. University of Alberta; Canadá
dc.journal.title
Industrial & Engineering Chemical Research

dc.relation.alternativeid
info:eu-repo/semantics/altIdentifier/doi/https://dx.doi.org/10.1021/acs.iecr.8b05420
dc.relation.alternativeid
info:eu-repo/semantics/altIdentifier/url/https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acs.iecr.8b05420
Archivos asociados