Artículo
Tracing sediment sources in an agriculture and livestock catchment of Argentina through the use of geochemical fingerprints
Torres Astorga, Romina Vanesa ; Velasco, Ricardo Hugo
; Velasco, Ricardo Hugo ; Resch, C.; Gruber, R.; Padilla, R.; Dercon, G.; Mabit, L.
; Resch, C.; Gruber, R.; Padilla, R.; Dercon, G.; Mabit, L.
 ; Velasco, Ricardo Hugo
; Velasco, Ricardo Hugo ; Resch, C.; Gruber, R.; Padilla, R.; Dercon, G.; Mabit, L.
; Resch, C.; Gruber, R.; Padilla, R.; Dercon, G.; Mabit, L.
Fecha de publicación:
01/2019
Editorial:
International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA)
Revista:
Soil Newsletter
ISSN:
1011-2650
Idioma:
Inglés
Tipo de recurso:
Artículo publicado
Clasificación temática:
Resumen
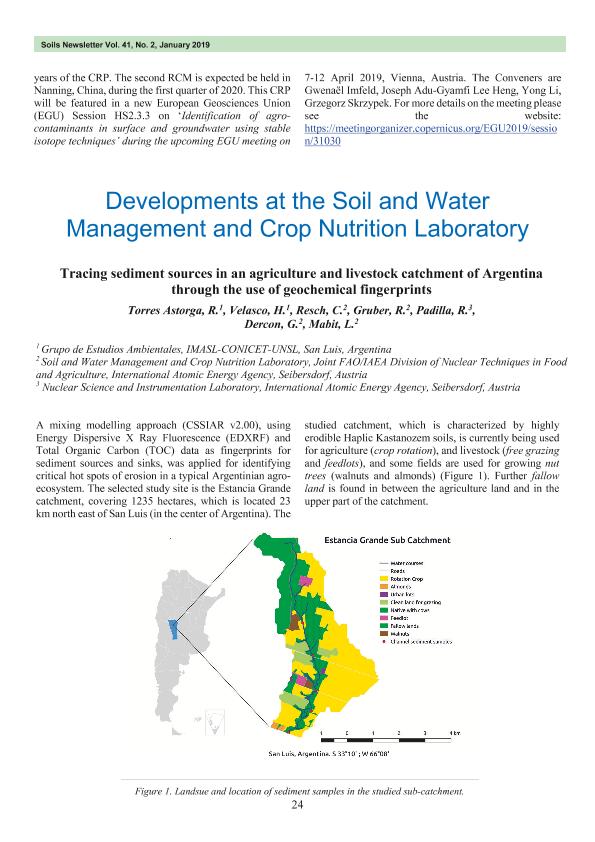
A mixing modelling approach (CSSIAR v2.00), using Energy Dispersive X Ray Fluorescence (EDXRF) and Total Organic Carbon (TOC) data as fingerprints for sediment sources and sinks, was applied for identifying critical hot spots of erosion in a typical Argentinian agro-ecosystem. The selected study site is the Estancia Grande catchment, covering 1235 hectares, which is located 23 km north east of San Luis (in the centre of Argentina). The studied catchment, which is characterized by highly erodible Haplic Kastanozem soils, is currently being used for agriculture (crop rotation), and livestock (free grazing and feedlots), and some fields are used for growing nut trees (walnuts and almonds) (Figure 1). Further fallow land is found in between the agriculture land and in the upper part of the catchment.
Palabras clave:
SOIL EROSION
,
FINGERPRINTS
,
EDFRX
,
GEOCHEMICAL
Archivos asociados
Licencia
Identificadores
Colecciones
Articulos(IMASL)
Articulos de INST. DE MATEMATICA APLICADA DE SAN LUIS
Articulos de INST. DE MATEMATICA APLICADA DE SAN LUIS
Citación
Torres Astorga, Romina Vanesa; Velasco, Ricardo Hugo; Resch, C.; Gruber, R.; Padilla, R.; et al.; Tracing sediment sources in an agriculture and livestock catchment of Argentina through the use of geochemical fingerprints; International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA); Soil Newsletter; 41; 2; 1-2019; 24-26
Compartir