Artículo
Extracellular Acidosis and mTOR Inhibition Drive the Differentiation of Human Monocyte-Derived Dendritic Cells
Erra Díaz, Fernando; Ochoa, Andrea Valeria; Merlotti Ippólito, Antonela ; Dantas, Ezequiel Carlos
; Dantas, Ezequiel Carlos ; Mazzitelli, Ignacio Gabriel
; Mazzitelli, Ignacio Gabriel ; Gonzalez Polo, Virginia
; Gonzalez Polo, Virginia ; Sabatte, Juan Atilio
; Sabatte, Juan Atilio ; Amigorena, Sebastián; Segura, Elodie; Geffner, Jorge Raúl
; Amigorena, Sebastián; Segura, Elodie; Geffner, Jorge Raúl
 ; Dantas, Ezequiel Carlos
; Dantas, Ezequiel Carlos ; Mazzitelli, Ignacio Gabriel
; Mazzitelli, Ignacio Gabriel ; Gonzalez Polo, Virginia
; Gonzalez Polo, Virginia ; Sabatte, Juan Atilio
; Sabatte, Juan Atilio ; Amigorena, Sebastián; Segura, Elodie; Geffner, Jorge Raúl
; Amigorena, Sebastián; Segura, Elodie; Geffner, Jorge Raúl
Fecha de publicación:
05/2020
Editorial:
Elsevier
Revista:
Cell Reports
ISSN:
2211-1247
Idioma:
Inglés
Tipo de recurso:
Artículo publicado
Clasificación temática:
Resumen
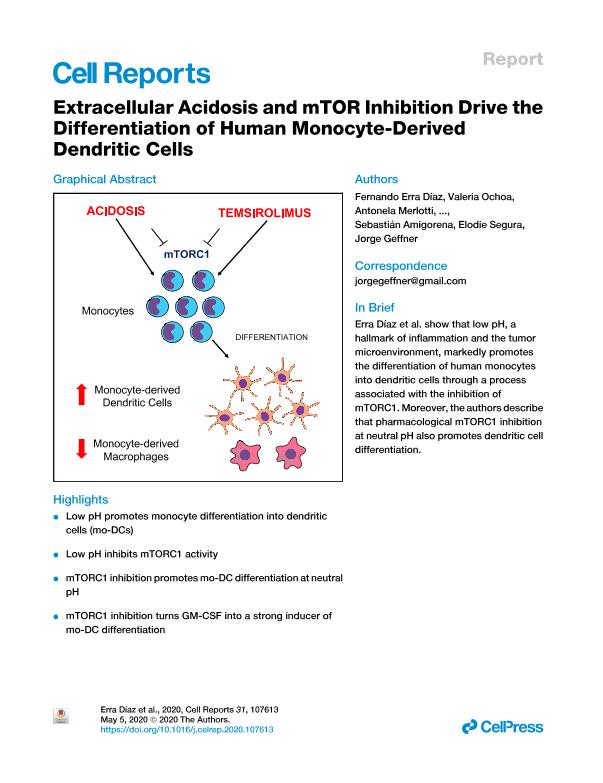
During inflammation, recruited monocytes can differentiate either into macrophages or dendritic cells (DCs); however, little is known about the environmental factors that determine this cell fate decision. Low extracellular pH is a hallmark of a variety of inflammatory processes and solid tumors. Here, we report that low pH dramatically promotes the differentiation of monocytes into DCs (monocyte-derived DCs [mo-DCs]). This process is associated with a reduction in glucose consumption and lactate production, the upregulation of mitochondrial respiratory chain genes, and the inhibition of mTORC1 activity. Interestingly, we also find that both serum starvation and pharmacological inhibition of mTORC1 markedly promote the differentiation of mo-DCs. Our study contributes to better understanding the mechanisms that govern the differentiation of monocytes into DCs and reveals the role of both extracellular pH and mTORC1 as master regulators of monocyte cell fate.
Palabras clave:
MONOCYTE
,
DENDRITIC CELLS
,
MTOR INHIBITION
,
INFLAMATION
Archivos asociados
Licencia
Identificadores
Colecciones
Articulos(INBIRS)
Articulos de INSTITUTO DE INVESTIGACIONES BIOMEDICAS EN RETROVIRUS Y SIDA
Articulos de INSTITUTO DE INVESTIGACIONES BIOMEDICAS EN RETROVIRUS Y SIDA
Citación
Erra Díaz, Fernando; Ochoa, Andrea Valeria; Merlotti Ippólito, Antonela; Dantas, Ezequiel Carlos; Mazzitelli, Ignacio Gabriel; et al.; Extracellular Acidosis and mTOR Inhibition Drive the Differentiation of Human Monocyte-Derived Dendritic Cells; Elsevier; Cell Reports; 31; 5; 5-2020; 1-18
Compartir
Altmétricas